数据处理工具
自然语言处理(NLP)是人工智能的重要分支,而数据处理是 NLP 项目成功的关键。
本文将系统介绍NLP数据处理全流程中必备的工具集,涵盖数据清洗、数值计算、特征工程、机器学习和可视化等核心环节。
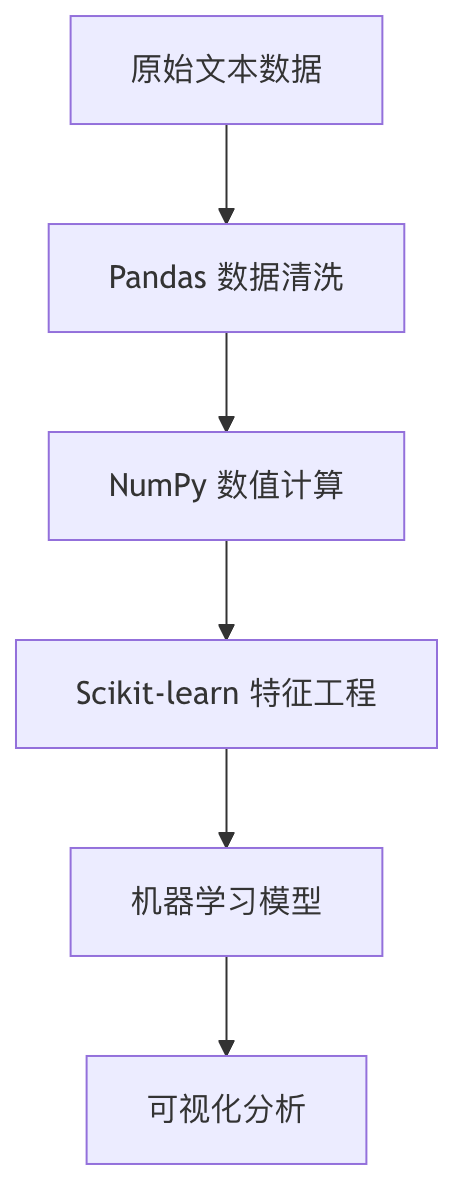
Pandas:数据清洗与预处理
Pandas 核心数据结构
Pandas 提供了两种主要数据结构,是NLP数据处理的基石:
| 数据结构 | 特点 | NLP应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| Series | 一维带标签数组 | 存储单个文本特征列 |
| DataFrame | 二维表格结构 | 存储整个文本数据集 |
常用文本处理操作
实例
import pandas as pd
# 创建示例数据
data = {'text': ['Hello World!', 'NLP is amazing', 'Python 3.8'],
'label': [1, 0, 1]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 1. 文本清洗
df['clean_text'] = df['text'].str.lower() # 转为小写
df['clean_text'] = df['clean_text'].str.replace('[^\w\s]', '') # 移除标点
# 2. 分词处理
df['tokens'] = df['clean_text'].str.split() # 按空格分词
# 3. 词频统计
word_counts = df['tokens'].explode().value_counts()
print(word_counts)
# 创建示例数据
data = {'text': ['Hello World!', 'NLP is amazing', 'Python 3.8'],
'label': [1, 0, 1]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 1. 文本清洗
df['clean_text'] = df['text'].str.lower() # 转为小写
df['clean_text'] = df['clean_text'].str.replace('[^\w\s]', '') # 移除标点
# 2. 分词处理
df['tokens'] = df['clean_text'].str.split() # 按空格分词
# 3. 词频统计
word_counts = df['tokens'].explode().value_counts()
print(word_counts)
高级文本处理技巧
- 正则表达式过滤:
df['text'].str.contains(r'\bNLP\b') - 停用词移除:结合NLTK或spaCy库
- 缺失值处理:
df.dropna()或df.fillna('UNK')
NumPy:高效数值计算
核心功能
NumPy 为NLP提供高效的数值计算能力:
- 多维数组:存储词向量、嵌入矩阵
- 广播机制:高效执行元素级运算
- 线性代数:矩阵分解、相似度计算
典型应用示例
实例
import numpy as np
# 创建词向量矩阵 (3个单词,每个5维)
word_vectors = np.array([
[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5], # 单词1
[0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0], # 单词2
[1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5] # 单词3
])
# 计算余弦相似度
def cosine_similarity(a, b):
return np.dot(a, b) / (np.linalg.norm(a) * (np.linalg.norm(b))
# 计算前两个词的相似度
sim = cosine_similarity(word_vectors[0], word_vectors[1])
print(f"相似度: {sim:.2f}")
# 创建词向量矩阵 (3个单词,每个5维)
word_vectors = np.array([
[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5], # 单词1
[0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0], # 单词2
[1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5] # 单词3
])
# 计算余弦相似度
def cosine_similarity(a, b):
return np.dot(a, b) / (np.linalg.norm(a) * (np.linalg.norm(b))
# 计算前两个词的相似度
sim = cosine_similarity(word_vectors[0], word_vectors[1])
print(f"相似度: {sim:.2f}")
性能优化技巧
- 使用
np.vectorize替代Python循环 - 利用
np.save/np.load高效存储大型矩阵 - 掌握
np.einsum进行复杂张量运算
Scikit-learn:机器学习管道
NLP特征提取
实例
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
corpus = [
'This is the first document.',
'This document is the second document.',
'And this is the third one.'
]
# 创建TF-IDF向量器
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus)
print(f"特征矩阵形状: {X.shape}")
print(f"特征词汇: {vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()}")
corpus = [
'This is the first document.',
'This document is the second document.',
'And this is the third one.'
]
# 创建TF-IDF向量器
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus)
print(f"特征矩阵形状: {X.shape}")
print(f"特征词汇: {vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()}")
完整NLP管道示例
实例
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 创建管道
nlp_pipeline = Pipeline([
('tfidf', TfidfVectorizer(max_features=1000)),
('clf', RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100))
])
# 示例数据准备
texts = ["good movie", "bad film", "great story"] * 100
labels = [1, 0, 1] * 100
# 训练测试分割
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(texts, labels)
# 训练模型
nlp_pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 评估
print(f"测试准确率: {nlp_pipeline.score(X_test, y_test):.2f}")
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 创建管道
nlp_pipeline = Pipeline([
('tfidf', TfidfVectorizer(max_features=1000)),
('clf', RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100))
])
# 示例数据准备
texts = ["good movie", "bad film", "great story"] * 100
labels = [1, 0, 1] * 100
# 训练测试分割
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(texts, labels)
# 训练模型
nlp_pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 评估
print(f"测试准确率: {nlp_pipeline.score(X_test, y_test):.2f}")
常用NLP组件
| 组件类别 | 主要类 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 特征提取 | CountVectorizer | 词袋模型 |
| TfidfVectorizer | TF-IDF加权 | |
| 文本预处理 | HashingVectorizer | 内存友好型特征提取 |
| 降维 | TruncatedSVD | 潜在语义分析 |
可视化工具
Matplotlib 基础可视化
实例
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 词频可视化示例
words = ['nlp', 'python', 'learning']
frequencies = [25, 40, 35]
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plt.bar(words, frequencies, color=['#3498db', '#2ecc71', '#e74c3c'])
plt.title('NLP术语频率分布')
plt.xlabel('术语')
plt.ylabel('出现次数')
plt.show()
# 词频可视化示例
words = ['nlp', 'python', 'learning']
frequencies = [25, 40, 35]
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plt.bar(words, frequencies, color=['#3498db', '#2ecc71', '#e74c3c'])
plt.title('NLP术语频率分布')
plt.xlabel('术语')
plt.ylabel('出现次数')
plt.show()
高级可视化库
Seaborn:统计图形更简单
实例
import seaborn as sns
sns.heatmap(tfidf_matrix, annot=True)
sns.heatmap(tfidf_matrix, annot=True)
WordCloud:生成词云
实例
from wordcloud import WordCloud
wordcloud = WordCloud().generate(' '.join(texts))
plt.imshow(wordcloud)
wordcloud = WordCloud().generate(' '.join(texts))
plt.imshow(wordcloud)
Plotly:交互式可视化
实例
import plotly.express as px
fig = px.scatter_3d(embeddings, x=0, y=1, z=2)
fig.show()
fig = px.scatter_3d(embeddings, x=0, y=1, z=2)
fig.show()
综合实践项目
情感分析完整流程
实例
# 1. 数据加载
df = pd.read_csv('reviews.csv')
# 2. 数据清洗
df['clean_text'] = df['text'].str.lower().str.replace('[^\w\s]', '')
# 3. 特征工程
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(max_features=5000)
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(df['clean_text'])
y = df['sentiment']
# 4. 模型训练
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
model = LinearSVC()
model.fit(X, y)
# 5. 可视化
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
y_pred = model.predict(X)
cm = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d')
df = pd.read_csv('reviews.csv')
# 2. 数据清洗
df['clean_text'] = df['text'].str.lower().str.replace('[^\w\s]', '')
# 3. 特征工程
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(max_features=5000)
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(df['clean_text'])
y = df['sentiment']
# 4. 模型训练
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
model = LinearSVC()
model.fit(X, y)
# 5. 可视化
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
y_pred = model.predict(X)
cm = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d')
性能优化技巧
- 并行处理:使用
n_jobs参数 - 特征选择:
SelectKBest减少维度 - 流水线缓存:
memory参数缓存中间结果
工具链扩展推荐
- NLTK:经典NLP工具包
- spaCy:工业级NLP处理
- Gensim:主题建模和词向量
- HuggingFace Transformers:预训练模型
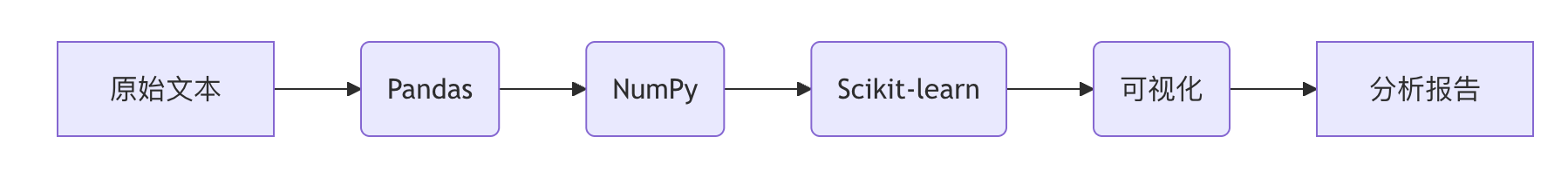
通过掌握这些工具的组合使用,您将能够高效处理大多数NLP数据处理任务,为更高级的NLP应用打下坚实基础。

点我分享笔记