Python 命令模式
命令模式是一种行为设计模式,它将一个请求封装成一个对象,从而使你可以用不同的请求对客户进行参数化。简单来说,命令模式把操作(比如打开文件、保存数据)包装成独立的对象,让你能够像处理数据一样处理操作。
生活中的类比
想象一下餐厅的点餐流程:
- 顾客(客户端)不需要知道厨师如何做菜
- 服务员(调用者)接收订单但不亲自烹饪
- 订单(命令对象)包含了具体的菜品信息
- 厨师(接收者)根据订单执行具体的烹饪操作
这种分工明确的模式就是命令模式在现实生活中的体现。
为什么需要命令模式
传统方式的局限性
在传统编程中,我们通常直接调用对象的方法:
实例
class Light:
def turn_on(self):
print("灯亮了")
def turn_off(self):
print("灯灭了")
# 直接调用
light = Light()
light.turn_on()
light.turn_off()
def turn_on(self):
print("灯亮了")
def turn_off(self):
print("灯灭了")
# 直接调用
light = Light()
light.turn_on()
light.turn_off()
这种方式存在几个问题:
- 紧耦合:调用者需要知道接收者的具体接口
- 难以扩展:添加新功能需要修改现有代码
- 不支持撤销/重做:操作执行后无法回退
命令模式的优势
命令模式通过引入中间层(命令对象)解决了上述问题,提供了:
- 解耦:调用者与接收者之间没有直接依赖
- 可扩展性:容易添加新的命令
- 支持撤销/重做:可以记录操作历史
- 队列支持:可以将命令放入队列延迟执行
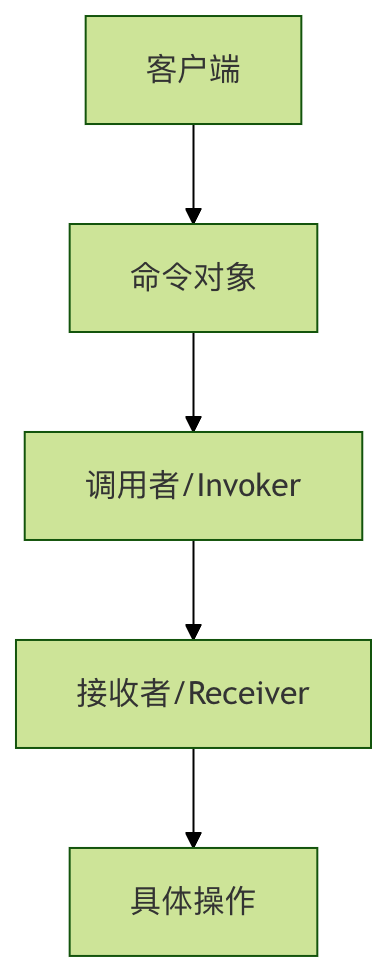
命令模式的核心组件
基本结构
命令模式包含四个核心角色:
| 角色 | 职责 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| Command(命令接口) | 声明执行操作的接口 | execute(), undo() |
| ConcreteCommand(具体命令) | 实现命令接口,绑定接收者 | LightOnCommand, LightOffCommand |
| Receiver(接收者) | 知道如何执行操作 | Light, TV |
| Invoker(调用者) | 存储并执行命令 | RemoteControl |
完整代码示例
基础实现
让我们通过一个智能家居的灯光控制例子来理解命令模式:
实例
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from typing import List
# 1. 命令接口
class Command(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def execute(self):
pass
@abstractmethod
def undo(self):
pass
# 2. 接收者 - 灯光设备
class Light:
def turn_on(self):
print("💡 灯光已打开")
def turn_off(self):
print("💡 灯光已关闭")
# 3. 具体命令 - 开灯命令
class LightOnCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, light: Light):
self.light = light
def execute(self):
self.light.turn_on()
def undo(self):
self.light.turn_off()
# 4. 具体命令 - 关灯命令
class LightOffCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, light: Light):
self.light = light
def execute(self):
self.light.turn_off()
def undo(self):
self.light.turn_on()
# 5. 调用者 - 遥控器
class RemoteControl:
def __init__(self):
self.command = None
self.history: List[Command] = []
def set_command(self, command: Command):
self.command = command
def press_button(self):
if self.command:
self.command.execute()
self.history.append(self.command)
def press_undo(self):
if self.history:
last_command = self.history.pop()
last_command.undo()
# 客户端代码
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建设备
living_room_light = Light()
# 创建命令
light_on = LightOnCommand(living_room_light)
light_off = LightOffCommand(living_room_light)
# 创建遥控器
remote = RemoteControl()
# 测试开灯
print("=== 测试开灯 ===")
remote.set_command(light_on)
remote.press_button()
# 测试关灯
print("\n=== 测试关灯 ===")
remote.set_command(light_off)
remote.press_button()
# 测试撤销
print("\n=== 测试撤销操作 ===")
remote.press_undo() # 撤销关灯,应该开灯
remote.press_undo() # 撤销开灯,应该关灯
from typing import List
# 1. 命令接口
class Command(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def execute(self):
pass
@abstractmethod
def undo(self):
pass
# 2. 接收者 - 灯光设备
class Light:
def turn_on(self):
print("💡 灯光已打开")
def turn_off(self):
print("💡 灯光已关闭")
# 3. 具体命令 - 开灯命令
class LightOnCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, light: Light):
self.light = light
def execute(self):
self.light.turn_on()
def undo(self):
self.light.turn_off()
# 4. 具体命令 - 关灯命令
class LightOffCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, light: Light):
self.light = light
def execute(self):
self.light.turn_off()
def undo(self):
self.light.turn_on()
# 5. 调用者 - 遥控器
class RemoteControl:
def __init__(self):
self.command = None
self.history: List[Command] = []
def set_command(self, command: Command):
self.command = command
def press_button(self):
if self.command:
self.command.execute()
self.history.append(self.command)
def press_undo(self):
if self.history:
last_command = self.history.pop()
last_command.undo()
# 客户端代码
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建设备
living_room_light = Light()
# 创建命令
light_on = LightOnCommand(living_room_light)
light_off = LightOffCommand(living_room_light)
# 创建遥控器
remote = RemoteControl()
# 测试开灯
print("=== 测试开灯 ===")
remote.set_command(light_on)
remote.press_button()
# 测试关灯
print("\n=== 测试关灯 ===")
remote.set_command(light_off)
remote.press_button()
# 测试撤销
print("\n=== 测试撤销操作 ===")
remote.press_undo() # 撤销关灯,应该开灯
remote.press_undo() # 撤销开灯,应该关灯
运行结果:
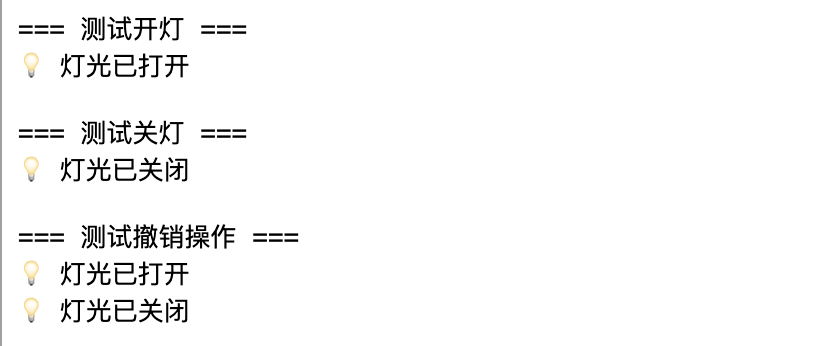
高级应用示例
支持多设备的万能遥控器
让我们扩展之前的例子,创建一个支持多种设备的万能遥控器:
实例
# 新增设备 - 电视
class TV:
def __init__(self, location: str):
self.location = location
self.is_on = False
self.volume = 50
def turn_on(self):
self.is_on = True
print(f"📺 {self.location}电视已打开")
def turn_off(self):
self.is_on = False
print(f"📺 {self.location}电视已关闭")
def set_volume(self, volume: int):
self.volume = volume
print(f"📺 {self.location}电视音量设置为 {volume}")
# 电视相关命令
class TVOnCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, tv: TV):
self.tv = tv
self.previous_volume = 50
def execute(self):
self.previous_volume = self.tv.volume
self.tv.turn_on()
def undo(self):
self.tv.turn_off()
self.tv.volume = self.previous_volume
class TVVolumeUpCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, tv: TV):
self.tv = tv
self.previous_volume = 50
def execute(self):
self.previous_volume = self.tv.volume
self.tv.set_volume(min(100, self.tv.volume + 10))
def undo(self):
self.tv.set_volume(self.previous_volume)
# 宏命令 - 一键执行多个命令
class MacroCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, commands: List[Command]):
self.commands = commands
def execute(self):
for command in self.commands:
command.execute()
def undo(self):
# 按相反顺序撤销
for command in reversed(self.commands):
command.undo()
# 改进的遥控器
class AdvancedRemoteControl:
def __init__(self, slot_count: int = 4):
self.on_commands: List[Command] = [None] * slot_count
self.off_commands: List[Command] = [None] * slot_count
self.history: List[Command] = []
def set_command(self, slot: int, on_command: Command, off_command: Command):
self.on_commands[slot] = on_command
self.off_commands[slot] = off_command
def press_on_button(self, slot: int):
if self.on_commands[slot]:
self.on_commands[slot].execute()
self.history.append(self.on_commands[slot])
def press_off_button(self, slot: int):
if self.off_commands[slot]:
self.off_commands[slot].execute()
self.history.append(self.off_commands[slot])
def press_undo(self):
if self.history:
last_command = self.history.pop()
last_command.undo()
# 测试高级遥控器
def test_advanced_remote():
print("=== 测试万能遥控器 ===")
# 创建设备
living_room_light = Light()
bedroom_tv = TV("卧室")
# 创建命令
light_on = LightOnCommand(living_room_light)
light_off = LightOffCommand(living_room_light)
tv_on = TVOnCommand(bedroom_tv)
tv_volume_up = TVVolumeUpCommand(bedroom_tv)
# 创建宏命令 - 影院模式
cinema_mode = MacroCommand([light_off, tv_on, tv_volume_up])
# 设置遥控器
remote = AdvancedRemoteControl()
remote.set_command(0, light_on, light_off) # 槽位0:灯光控制
remote.set_command(1, tv_on, TVOnCommand(bedroom_tv)) # 槽位1:电视控制
remote.set_command(2, cinema_mode, light_on) # 槽位2:影院模式
# 测试各种功能
print("\n1. 打开灯光:")
remote.press_on_button(0)
print("\n2. 开启影院模式:")
remote.press_on_button(2)
print("\n3. 撤销操作:")
remote.press_undo()
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_advanced_remote()
class TV:
def __init__(self, location: str):
self.location = location
self.is_on = False
self.volume = 50
def turn_on(self):
self.is_on = True
print(f"📺 {self.location}电视已打开")
def turn_off(self):
self.is_on = False
print(f"📺 {self.location}电视已关闭")
def set_volume(self, volume: int):
self.volume = volume
print(f"📺 {self.location}电视音量设置为 {volume}")
# 电视相关命令
class TVOnCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, tv: TV):
self.tv = tv
self.previous_volume = 50
def execute(self):
self.previous_volume = self.tv.volume
self.tv.turn_on()
def undo(self):
self.tv.turn_off()
self.tv.volume = self.previous_volume
class TVVolumeUpCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, tv: TV):
self.tv = tv
self.previous_volume = 50
def execute(self):
self.previous_volume = self.tv.volume
self.tv.set_volume(min(100, self.tv.volume + 10))
def undo(self):
self.tv.set_volume(self.previous_volume)
# 宏命令 - 一键执行多个命令
class MacroCommand(Command):
def __init__(self, commands: List[Command]):
self.commands = commands
def execute(self):
for command in self.commands:
command.execute()
def undo(self):
# 按相反顺序撤销
for command in reversed(self.commands):
command.undo()
# 改进的遥控器
class AdvancedRemoteControl:
def __init__(self, slot_count: int = 4):
self.on_commands: List[Command] = [None] * slot_count
self.off_commands: List[Command] = [None] * slot_count
self.history: List[Command] = []
def set_command(self, slot: int, on_command: Command, off_command: Command):
self.on_commands[slot] = on_command
self.off_commands[slot] = off_command
def press_on_button(self, slot: int):
if self.on_commands[slot]:
self.on_commands[slot].execute()
self.history.append(self.on_commands[slot])
def press_off_button(self, slot: int):
if self.off_commands[slot]:
self.off_commands[slot].execute()
self.history.append(self.off_commands[slot])
def press_undo(self):
if self.history:
last_command = self.history.pop()
last_command.undo()
# 测试高级遥控器
def test_advanced_remote():
print("=== 测试万能遥控器 ===")
# 创建设备
living_room_light = Light()
bedroom_tv = TV("卧室")
# 创建命令
light_on = LightOnCommand(living_room_light)
light_off = LightOffCommand(living_room_light)
tv_on = TVOnCommand(bedroom_tv)
tv_volume_up = TVVolumeUpCommand(bedroom_tv)
# 创建宏命令 - 影院模式
cinema_mode = MacroCommand([light_off, tv_on, tv_volume_up])
# 设置遥控器
remote = AdvancedRemoteControl()
remote.set_command(0, light_on, light_off) # 槽位0:灯光控制
remote.set_command(1, tv_on, TVOnCommand(bedroom_tv)) # 槽位1:电视控制
remote.set_command(2, cinema_mode, light_on) # 槽位2:影院模式
# 测试各种功能
print("\n1. 打开灯光:")
remote.press_on_button(0)
print("\n2. 开启影院模式:")
remote.press_on_button(2)
print("\n3. 撤销操作:")
remote.press_undo()
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_advanced_remote()
命令模式的参数和选项
命令接口的扩展
在实际应用中,命令接口可以根据需要扩展更多功能:
实例
class AdvancedCommand(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def execute(self):
"""执行命令"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def undo(self):
"""撤销命令"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def redo(self):
"""重做命令"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def can_execute(self) -> bool:
"""检查命令是否可以执行"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def get_description(self) -> str:
"""获取命令描述"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def execute(self):
"""执行命令"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def undo(self):
"""撤销命令"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def redo(self):
"""重做命令"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def can_execute(self) -> bool:
"""检查命令是否可以执行"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def get_description(self) -> str:
"""获取命令描述"""
pass
命令队列和延迟执行
命令模式天然支持命令队列,这在很多场景下非常有用:
实例
class CommandQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue: List[Command] = []
def add_command(self, command: Command):
self.queue.append(command)
def process_commands(self):
while self.queue:
command = self.queue.pop(0)
if command.can_execute():
command.execute()
def clear(self):
self.queue.clear()
def __init__(self):
self.queue: List[Command] = []
def add_command(self, command: Command):
self.queue.append(command)
def process_commands(self):
while self.queue:
command = self.queue.pop(0)
if command.can_execute():
command.execute()
def clear(self):
self.queue.clear()
实践练习
练习 1:实现空调控制系统
尝试实现一个空调控制系统的命令模式:
实例
# 你的代码在这里
class AirConditioner:
def __init__(self):
self.temperature = 26
self.is_on = False
def turn_on(self):
# 实现打开空调
pass
def turn_off(self):
# 实现关闭空调
pass
def set_temperature(self, temp: int):
# 实现设置温度
pass
# 实现空调相关的命令类
# AirConditionerOnCommand
# AirConditionerOffCommand
# TemperatureUpCommand
# TemperatureDownCommand
class AirConditioner:
def __init__(self):
self.temperature = 26
self.is_on = False
def turn_on(self):
# 实现打开空调
pass
def turn_off(self):
# 实现关闭空调
pass
def set_temperature(self, temp: int):
# 实现设置温度
pass
# 实现空调相关的命令类
# AirConditionerOnCommand
# AirConditionerOffCommand
# TemperatureUpCommand
# TemperatureDownCommand
练习 2:实现文本编辑器的撤销功能
创建一个简单的文本编辑器,支持输入文本和撤销操作:
实例
class TextEditor:
def __init__(self):
self.content = ""
def add_text(self, text: str):
# 实现添加文本
pass
def delete_text(self, length: int):
# 实现删除文本
pass
# 实现文本编辑命令
# AddTextCommand
# DeleteTextCommand
def __init__(self):
self.content = ""
def add_text(self, text: str):
# 实现添加文本
pass
def delete_text(self, length: int):
# 实现删除文本
pass
# 实现文本编辑命令
# AddTextCommand
# DeleteTextCommand
常见问题解答
Q: 命令模式适用于什么场景?
A: 命令模式特别适合以下场景:
- 需要将操作参数化(如按钮绑定不同功能)
- 需要支持撤销/重做功能
- 需要将操作放入队列中延迟执行
- 需要记录操作日志
- 需要支持事务操作
Q: 命令模式的缺点是什么?
A: 主要缺点包括:
- 可能会创建大量的命令类
- 增加了代码的复杂度
- 对于简单操作可能显得过于繁琐
Q: 如何选择是否使用命令模式?
A: 考虑以下几点:
- 如果只需要简单的方法调用,不要使用命令模式
- 如果需要撤销/重做功能,强烈推荐使用
- 如果系统需要高度解耦,命令模式是很好的选择
- 如果操作需要排队或日志记录,命令模式很合适
总结
命令模式通过将操作封装成对象,实现了调用者与接收者的解耦,提供了强大的扩展能力。虽然会增加一些代码复杂度,但在需要撤销/重做、操作队列、日志记录等场景下,命令模式是不可或缺的设计模式。
关键要点:
- 命令模式将"做什么"和"谁来做"分离
- 支持撤销、重做、队列等高级功能
- 易于扩展新的命令
- 在 GUI 应用、事务系统、游戏开发中广泛应用

点我分享笔记