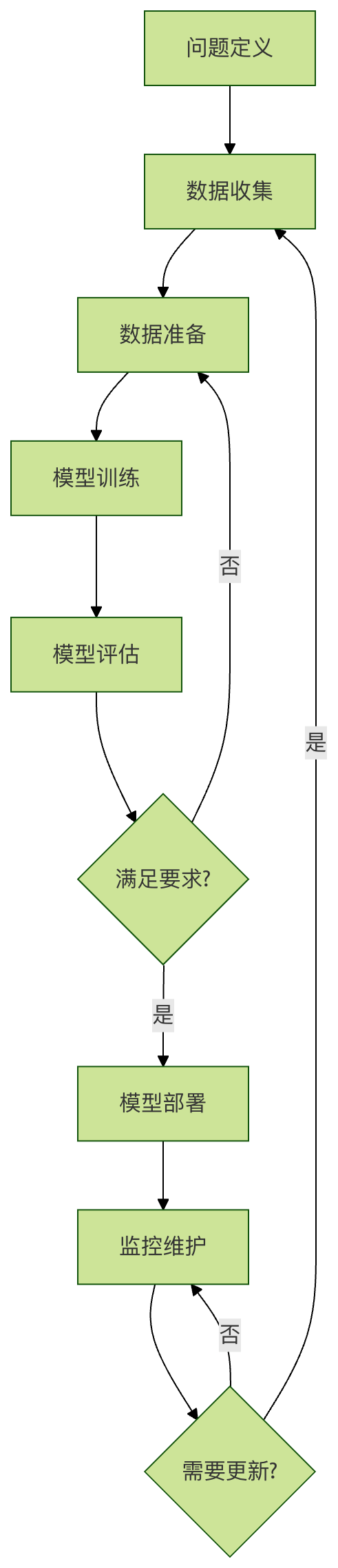
机器学习项目生命周期
机器学习项目就像建造一座房子,需要从设计图纸到施工再到验收的完整过程,每个环节都至关重要,缺一不可。
机器学习流程的六个核心阶段:
- 问题定义:明确要解决什么问题
- 数据收集:获取相关数据
- 数据准备:清洗和预处理数据
- 模型训练:选择算法并训练模型
- 模型评估:评估模型性能
- 模型部署:将模型投入使用
第一阶段:问题定义
明确业务问题
问题定义是机器学习项目最重要的起点,就像导航前需要明确目的地一样。
关键问题
我们要解决什么问题?
- 分类问题:判断邮件是否为垃圾邮件
- 回归问题:预测房价
- 聚类问题:客户分群
- 异常检测:发现信用卡欺诈
为什么这个问题重要?
- 业务价值:提高效率、降低成本、增加收入
- 用户价值:改善体验、提供个性化服务
成功的标准是什么?
- 量化指标:准确率达到 90% 以上
- 业务指标:转化率提升 20%
问题定义示例
实例
# 问题定义示例:电商推荐系统
class ProblemDefinition:
def __init__(self):
# 业务问题
self.business_problem = "用户购买转化率低,需要提高推荐精准度"
# 技术问题
self.technical_problem = "基于用户行为预测用户可能购买的商品"
# 问题类型
self.problem_type = "推荐系统(分类+排序)"
# 成功标准
self.success_criteria = {
"点击率提升": "15%",
"转化率提升": "10%",
"推荐准确率": "80%"
}
# 约束条件
self.constraints = {
"响应时间": "< 100ms",
"数据隐私": "符合 GDPR 要求",
"计算资源": "现有服务器配置"
}
def define_features_and_labels(self):
"""定义特征和标签"""
features = {
"用户特征": ["年龄", "性别", "购买历史", "浏览行为"],
"商品特征": ["类别", "价格", "评分", "库存"],
"上下文特征": ["时间", "设备", "地理位置"]
}
labels = {
"主要标签": "是否点击",
"次要标签": "是否购买",
"辅助标签": "停留时间"
}
return features, labels
def print_definition(self):
"""打印问题定义"""
print("=" * 50)
print("机器学习问题定义")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"业务问题:{self.business_problem}")
print(f"技术问题:{self.technical_problem}")
print(f"问题类型:{self.problem_type}")
print("\n成功标准:")
for metric, target in self.success_criteria.items():
print(f" {metric}:{target}")
print("\n约束条件:")
for constraint, limit in self.constraints.items():
print(f" {constraint}:{limit}")
features, labels = self.define_features_and_labels()
print("\n特征定义:")
for category, items in features.items():
print(f" {category}:{', '.join(items)}")
print("\n标签定义:")
for label_type, label_name in labels.items():
print(f" {label_type}:{label_name}")
# 使用示例
problem = ProblemDefinition()
problem.print_definition()
class ProblemDefinition:
def __init__(self):
# 业务问题
self.business_problem = "用户购买转化率低,需要提高推荐精准度"
# 技术问题
self.technical_problem = "基于用户行为预测用户可能购买的商品"
# 问题类型
self.problem_type = "推荐系统(分类+排序)"
# 成功标准
self.success_criteria = {
"点击率提升": "15%",
"转化率提升": "10%",
"推荐准确率": "80%"
}
# 约束条件
self.constraints = {
"响应时间": "< 100ms",
"数据隐私": "符合 GDPR 要求",
"计算资源": "现有服务器配置"
}
def define_features_and_labels(self):
"""定义特征和标签"""
features = {
"用户特征": ["年龄", "性别", "购买历史", "浏览行为"],
"商品特征": ["类别", "价格", "评分", "库存"],
"上下文特征": ["时间", "设备", "地理位置"]
}
labels = {
"主要标签": "是否点击",
"次要标签": "是否购买",
"辅助标签": "停留时间"
}
return features, labels
def print_definition(self):
"""打印问题定义"""
print("=" * 50)
print("机器学习问题定义")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"业务问题:{self.business_problem}")
print(f"技术问题:{self.technical_problem}")
print(f"问题类型:{self.problem_type}")
print("\n成功标准:")
for metric, target in self.success_criteria.items():
print(f" {metric}:{target}")
print("\n约束条件:")
for constraint, limit in self.constraints.items():
print(f" {constraint}:{limit}")
features, labels = self.define_features_and_labels()
print("\n特征定义:")
for category, items in features.items():
print(f" {category}:{', '.join(items)}")
print("\n标签定义:")
for label_type, label_name in labels.items():
print(f" {label_type}:{label_name}")
# 使用示例
problem = ProblemDefinition()
problem.print_definition()
第二阶段:数据收集
数据来源
数据是机器学习的燃料,没有合适的数据再好的算法也无法发挥作用。
常见数据来源
- 内部数据:公司业务数据、用户行为数据
- 外部数据:公开数据集、第三方数据服务
- 网络爬虫:网页数据、社交媒体数据
- 传感器数据:IoT 设备、监控系统
数据收集示例
实例
# 数据收集示例:模拟多种数据源
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class DataCollector:
def __init__(self):
self.collected_data = {}
def collect_user_data(self, n_users=1000):
"""收集用户数据"""
np.random.seed(42)
user_data = {
'user_id': range(1, n_users + 1),
'age': np.random.randint(18, 65, n_users),
'gender': np.random.choice(['男', '女'], n_users),
'city': np.random.choice(['北京', '上海', '广州', '深圳'], n_users),
'registration_date': [
datetime.now() - timedelta(days=np.random.randint(1, 365))
for _ in range(n_users)
]
}
self.collected_data['users'] = pd.DataFrame(user_data)
print(f"收集了 {len(user_data['user_id'])} 条用户数据")
return self.collected_data['users']
def collect_behavior_data(self, n_behaviors=5000):
"""收集用户行为数据"""
np.random.seed(42)
user_ids = np.random.choice(range(1, 1001), n_behaviors)
product_ids = np.random.choice(range(1, 501), n_behaviors)
behavior_data = {
'behavior_id': range(1, n_behaviors + 1),
'user_id': user_ids,
'product_id': product_ids,
'behavior_type': np.random.choice(
['浏览', '点击', '加购物车', '购买'], n_behaviors,
p=[0.4, 0.3, 0.2, 0.1]
),
'timestamp': [
datetime.now() - timedelta(minutes=np.random.randint(1, 10080))
for _ in range(n_behaviors)
],
'duration': np.random.exponential(30, n_behaviors) # 停留时间(秒)
}
self.collected_data['behaviors'] = pd.DataFrame(behavior_data)
print(f"收集了 {len(behavior_data['behavior_id'])} 条行为数据")
return self.collected_data['behaviors']
def collect_product_data(self, n_products=500):
"""收集商品数据"""
np.random.seed(42)
categories = ['电子产品', '服装', '食品', '家居', '图书']
product_data = {
'product_id': range(1, n_products + 1),
'category': np.random.choice(categories, n_products),
'price': np.random.uniform(10, 1000, n_products),
'rating': np.random.uniform(3.0, 5.0, n_products),
'stock': np.random.randint(0, 1000, n_products)
}
self.collected_data['products'] = pd.DataFrame(product_data)
print(f"收集了 {len(product_data['product_id'])} 条商品数据")
return self.collected_data['products']
def get_data_summary(self):
"""获取数据摘要"""
print("\n数据收集摘要:")
for name, df in self.collected_data.items():
print(f"\n{name} 数据集:")
print(f" 形状:{df.shape}")
print(f" 列名:{list(df.columns)}")
print(f" 缺失值:{df.isnull().sum().sum()}")
print(f" 示例数据:")
print(df.head(2))
# 使用示例
collector = DataCollector()
collector.collect_user_data()
collector.collect_behavior_data()
collector.collect_product_data()
collector.get_data_summary()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class DataCollector:
def __init__(self):
self.collected_data = {}
def collect_user_data(self, n_users=1000):
"""收集用户数据"""
np.random.seed(42)
user_data = {
'user_id': range(1, n_users + 1),
'age': np.random.randint(18, 65, n_users),
'gender': np.random.choice(['男', '女'], n_users),
'city': np.random.choice(['北京', '上海', '广州', '深圳'], n_users),
'registration_date': [
datetime.now() - timedelta(days=np.random.randint(1, 365))
for _ in range(n_users)
]
}
self.collected_data['users'] = pd.DataFrame(user_data)
print(f"收集了 {len(user_data['user_id'])} 条用户数据")
return self.collected_data['users']
def collect_behavior_data(self, n_behaviors=5000):
"""收集用户行为数据"""
np.random.seed(42)
user_ids = np.random.choice(range(1, 1001), n_behaviors)
product_ids = np.random.choice(range(1, 501), n_behaviors)
behavior_data = {
'behavior_id': range(1, n_behaviors + 1),
'user_id': user_ids,
'product_id': product_ids,
'behavior_type': np.random.choice(
['浏览', '点击', '加购物车', '购买'], n_behaviors,
p=[0.4, 0.3, 0.2, 0.1]
),
'timestamp': [
datetime.now() - timedelta(minutes=np.random.randint(1, 10080))
for _ in range(n_behaviors)
],
'duration': np.random.exponential(30, n_behaviors) # 停留时间(秒)
}
self.collected_data['behaviors'] = pd.DataFrame(behavior_data)
print(f"收集了 {len(behavior_data['behavior_id'])} 条行为数据")
return self.collected_data['behaviors']
def collect_product_data(self, n_products=500):
"""收集商品数据"""
np.random.seed(42)
categories = ['电子产品', '服装', '食品', '家居', '图书']
product_data = {
'product_id': range(1, n_products + 1),
'category': np.random.choice(categories, n_products),
'price': np.random.uniform(10, 1000, n_products),
'rating': np.random.uniform(3.0, 5.0, n_products),
'stock': np.random.randint(0, 1000, n_products)
}
self.collected_data['products'] = pd.DataFrame(product_data)
print(f"收集了 {len(product_data['product_id'])} 条商品数据")
return self.collected_data['products']
def get_data_summary(self):
"""获取数据摘要"""
print("\n数据收集摘要:")
for name, df in self.collected_data.items():
print(f"\n{name} 数据集:")
print(f" 形状:{df.shape}")
print(f" 列名:{list(df.columns)}")
print(f" 缺失值:{df.isnull().sum().sum()}")
print(f" 示例数据:")
print(df.head(2))
# 使用示例
collector = DataCollector()
collector.collect_user_data()
collector.collect_behavior_data()
collector.collect_product_data()
collector.get_data_summary()
第三阶段:数据准备
数据准备的重要性
数据准备占机器学习项目 60-80% 的时间,就像做菜前的准备工作一样重要。
数据准备的主要任务
- 数据清洗:处理缺失值、异常值、重复值
- 特征工程:创建新特征、选择重要特征
- 数据转换:标准化、归一化、编码
- 数据划分:训练集、验证集、测试集
数据准备示例
实例
# 数据准备示例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
class DataPreparer:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data.copy()
self.processed_data = None
def clean_data(self):
"""数据清洗"""
print("开始数据清洗...")
# 1. 处理缺失值
print(f"处理前缺失值数量:{self.data.isnull().sum().sum()}")
# 数值列用均值填充
numeric_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=[np.number]).columns
for col in numeric_columns:
if self.data[col].isnull().sum() > 0:
self.data[col].fillna(self.data[col].mean(), inplace=True)
# 类别列用众数填充
categorical_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=['object']).columns
for col in categorical_columns:
if self.data[col].isnull().sum() > 0:
mode_val = self.data[col].mode()[0]
self.data[col].fillna(mode_val, inplace=True)
print(f"处理后缺失值数量:{self.data.isnull().sum().sum()}")
# 2. 处理重复值
duplicates_before = self.data.duplicated().sum()
self.data.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)
duplicates_after = self.data.duplicated().sum()
print(f"删除重复值:{duplicates_before - duplicates_after} 条")
# 3. 处理异常值(简单方法:使用 IQR)
for col in numeric_columns:
Q1 = self.data[col].quantile(0.25)
Q3 = self.data[col].quantile(0.75)
IQR = Q3 - Q1
lower_bound = Q1 - 1.5 * IQR
upper_bound = Q3 + 1.5 * IQR
outliers = ((self.data[col] < lower_bound) |
(self.data[col] > upper_bound)).sum()
if outliers > 0:
# 用边界值替换异常值
self.data[col] = self.data[col].clip(lower_bound, upper_bound)
print(f"处理 {col} 列的 {outliers} 个异常值")
return self.data
def feature_engineering(self):
"""特征工程"""
print("\n开始特征工程...")
# 1. 创建新特征(示例)
if 'price' in self.data.columns and 'rating' in self.data.columns:
# 创建性价比特征
self.data['price_per_rating'] = self.data['price'] / self.data['rating']
print("创建新特征:price_per_rating")
# 2. 特征选择(简单示例:移除低方差特征)
numeric_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=[np.number]).columns
low_variance_features = []
for col in numeric_columns:
if self.data[col].var() < 0.01: # 方差阈值
low_variance_features.append(col)
if low_variance_features:
self.data.drop(columns=low_variance_features, inplace=True)
print(f"移除低方差特征:{low_variance_features}")
return self.data
def transform_data(self):
"""数据转换"""
print("\n开始数据转换...")
# 1. 编码类别变量
categorical_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=['object']).columns
label_encoders = {}
for col in categorical_columns:
le = LabelEncoder()
self.data[col] = le.fit_transform(self.data[col])
label_encoders[col] = le
print(f"编码类别变量:{col}")
# 2. 标准化数值变量
numeric_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=[np.number]).columns
scaler = StandardScaler()
if len(numeric_columns) > 0:
self.data[numeric_columns] = scaler.fit_transform(self.data[numeric_columns])
print(f"标准化数值变量:{list(numeric_columns)}")
return self.data, label_encoders, scaler
def split_data(self, target_column, test_size=0.2, val_size=0.2):
"""数据划分"""
print(f"\n开始数据划分(测试集比例:{test_size},验证集比例:{val_size})...")
X = self.data.drop(columns=[target_column])
y = self.data[target_column]
# 首先分离出测试集
X_temp, X_test, y_temp, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=test_size, random_state=42
)
# 再从剩余数据中分离出验证集
val_size_adjusted = val_size / (1 - test_size)
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(
X_temp, y_temp, test_size=val_size_adjusted, random_state=42
)
print(f"训练集大小:{X_train.shape[0]}")
print(f"验证集大小:{X_val.shape[0]}")
print(f"测试集大小:{X_test.shape[0]}")
return {
'X_train': X_train, 'y_train': y_train,
'X_val': X_val, 'y_val': y_val,
'X_test': X_test, 'y_test': y_test
}
def prepare_pipeline(self, target_column):
"""完整的数据准备流水线"""
print("=" * 50)
print("数据准备流水线")
print("=" * 50)
# 1. 数据清洗
self.clean_data()
# 2. 特征工程
self.feature_engineering()
# 3. 数据转换
processed_data, encoders, scaler = self.transform_data()
# 4. 数据划分
splits = self.split_data(target_column)
self.processed_data = processed_data
return splits, encoders, scaler
# 创建示例数据并演示数据准备
np.random.seed(42)
sample_data = pd.DataFrame({
'age': np.random.randint(18, 65, 1000),
'income': np.random.normal(50000, 15000, 1000),
'gender': np.random.choice(['男', '女'], 1000),
'city': np.random.choice(['北京', '上海', '广州'], 1000),
'target': np.random.choice([0, 1], 1000)
})
# 添加一些缺失值和异常值
sample_data.loc[np.random.choice(1000, 50), 'income'] = np.nan
sample_data.loc[np.random.choice(1000, 20), 'age'] = np.random.randint(100, 150)
preparer = DataPreparer(sample_data)
splits, encoders, scaler = preparer.prepare_pipeline('target')
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
class DataPreparer:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data.copy()
self.processed_data = None
def clean_data(self):
"""数据清洗"""
print("开始数据清洗...")
# 1. 处理缺失值
print(f"处理前缺失值数量:{self.data.isnull().sum().sum()}")
# 数值列用均值填充
numeric_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=[np.number]).columns
for col in numeric_columns:
if self.data[col].isnull().sum() > 0:
self.data[col].fillna(self.data[col].mean(), inplace=True)
# 类别列用众数填充
categorical_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=['object']).columns
for col in categorical_columns:
if self.data[col].isnull().sum() > 0:
mode_val = self.data[col].mode()[0]
self.data[col].fillna(mode_val, inplace=True)
print(f"处理后缺失值数量:{self.data.isnull().sum().sum()}")
# 2. 处理重复值
duplicates_before = self.data.duplicated().sum()
self.data.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)
duplicates_after = self.data.duplicated().sum()
print(f"删除重复值:{duplicates_before - duplicates_after} 条")
# 3. 处理异常值(简单方法:使用 IQR)
for col in numeric_columns:
Q1 = self.data[col].quantile(0.25)
Q3 = self.data[col].quantile(0.75)
IQR = Q3 - Q1
lower_bound = Q1 - 1.5 * IQR
upper_bound = Q3 + 1.5 * IQR
outliers = ((self.data[col] < lower_bound) |
(self.data[col] > upper_bound)).sum()
if outliers > 0:
# 用边界值替换异常值
self.data[col] = self.data[col].clip(lower_bound, upper_bound)
print(f"处理 {col} 列的 {outliers} 个异常值")
return self.data
def feature_engineering(self):
"""特征工程"""
print("\n开始特征工程...")
# 1. 创建新特征(示例)
if 'price' in self.data.columns and 'rating' in self.data.columns:
# 创建性价比特征
self.data['price_per_rating'] = self.data['price'] / self.data['rating']
print("创建新特征:price_per_rating")
# 2. 特征选择(简单示例:移除低方差特征)
numeric_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=[np.number]).columns
low_variance_features = []
for col in numeric_columns:
if self.data[col].var() < 0.01: # 方差阈值
low_variance_features.append(col)
if low_variance_features:
self.data.drop(columns=low_variance_features, inplace=True)
print(f"移除低方差特征:{low_variance_features}")
return self.data
def transform_data(self):
"""数据转换"""
print("\n开始数据转换...")
# 1. 编码类别变量
categorical_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=['object']).columns
label_encoders = {}
for col in categorical_columns:
le = LabelEncoder()
self.data[col] = le.fit_transform(self.data[col])
label_encoders[col] = le
print(f"编码类别变量:{col}")
# 2. 标准化数值变量
numeric_columns = self.data.select_dtypes(include=[np.number]).columns
scaler = StandardScaler()
if len(numeric_columns) > 0:
self.data[numeric_columns] = scaler.fit_transform(self.data[numeric_columns])
print(f"标准化数值变量:{list(numeric_columns)}")
return self.data, label_encoders, scaler
def split_data(self, target_column, test_size=0.2, val_size=0.2):
"""数据划分"""
print(f"\n开始数据划分(测试集比例:{test_size},验证集比例:{val_size})...")
X = self.data.drop(columns=[target_column])
y = self.data[target_column]
# 首先分离出测试集
X_temp, X_test, y_temp, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=test_size, random_state=42
)
# 再从剩余数据中分离出验证集
val_size_adjusted = val_size / (1 - test_size)
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(
X_temp, y_temp, test_size=val_size_adjusted, random_state=42
)
print(f"训练集大小:{X_train.shape[0]}")
print(f"验证集大小:{X_val.shape[0]}")
print(f"测试集大小:{X_test.shape[0]}")
return {
'X_train': X_train, 'y_train': y_train,
'X_val': X_val, 'y_val': y_val,
'X_test': X_test, 'y_test': y_test
}
def prepare_pipeline(self, target_column):
"""完整的数据准备流水线"""
print("=" * 50)
print("数据准备流水线")
print("=" * 50)
# 1. 数据清洗
self.clean_data()
# 2. 特征工程
self.feature_engineering()
# 3. 数据转换
processed_data, encoders, scaler = self.transform_data()
# 4. 数据划分
splits = self.split_data(target_column)
self.processed_data = processed_data
return splits, encoders, scaler
# 创建示例数据并演示数据准备
np.random.seed(42)
sample_data = pd.DataFrame({
'age': np.random.randint(18, 65, 1000),
'income': np.random.normal(50000, 15000, 1000),
'gender': np.random.choice(['男', '女'], 1000),
'city': np.random.choice(['北京', '上海', '广州'], 1000),
'target': np.random.choice([0, 1], 1000)
})
# 添加一些缺失值和异常值
sample_data.loc[np.random.choice(1000, 50), 'income'] = np.nan
sample_data.loc[np.random.choice(1000, 20), 'age'] = np.random.randint(100, 150)
preparer = DataPreparer(sample_data)
splits, encoders, scaler = preparer.prepare_pipeline('target')
第四阶段:模型训练
模型选择策略
选择合适的模型是成功的关键,就像选择合适的工具来完成工作一样。
模型选择考虑因素
- 问题类型:分类、回归、聚类等
- 数据特征:数据量、特征数量、数据类型
- 性能要求:准确率、速度、可解释性
- 资源约束:计算资源、时间限制
模型训练示例
实例
# 模型训练示例
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression, LinearRegression
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.svm import SVC, SVR
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, mean_squared_error, classification_report
class ModelTrainer:
def __init__(self):
self.models = {}
self.trained_models = {}
def register_model(self, name, model, problem_type):
"""注册模型"""
self.models[name] = {
'model': model,
'problem_type': problem_type
}
print(f"注册模型:{name}({problem_type})")
def train_single_model(self, name, X_train, y_train):
"""训练单个模型"""
if name not in self.models:
raise ValueError(f"模型 {name} 未注册")
model_info = self.models[name]
model = model_info['model']
print(f"\n训练模型:{name}")
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
self.trained_models[name] = model
print(f"模型 {name} 训练完成")
return model
def train_all_models(self, X_train, y_train):
"""训练所有注册的模型"""
print("\n开始训练所有模型...")
for name in self.models.keys():
try:
self.train_single_model(name, X_train, y_train)
except Exception as e:
print(f"训练模型 {name} 时出错:{e}")
return self.trained_models
def evaluate_models(self, X_test, y_test):
"""评估所有训练好的模型"""
print("\n模型评估结果:")
print("-" * 50)
results = {}
for name, model in self.trained_models.items():
problem_type = self.models[name]['problem_type']
# 预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# 根据问题类型选择评估指标
if problem_type == 'classification':
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
results[name] = {'accuracy': accuracy}
print(f"{name}: 准确率 = {accuracy:.4f}")
# 详细报告
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
elif problem_type == 'regression':
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
rmse = np.sqrt(mse)
results[name] = {'mse': mse, 'rmse': rmse}
print(f"{name}: MSE = {mse:.4f}, RMSE = {rmse:.4f}")
print("-" * 50)
return results
def get_best_model(self, results, metric='accuracy'):
"""获取最佳模型"""
if not results:
return None
best_model_name = max(results.keys(), key=lambda x: results[x].get(metric, 0))
best_score = results[best_model_name][metric]
print(f"\n最佳模型:{best_model_name}({metric} = {best_score:.4f})")
return best_model_name, self.trained_models[best_model_name]
# 使用示例
trainer = ModelTrainer()
# 注册不同类型的模型
trainer.register_model('逻辑回归', LogisticRegression(random_state=42), 'classification')
trainer.register_model('随机森林', RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42), 'classification')
trainer.register_model('支持向量机', SVC(random_state=42), 'classification')
# 创建训练数据
X_train = splits['X_train']
y_train = splits['y_train']
X_test = splits['X_test']
y_test = splits['y_test']
# 训练所有模型
trained_models = trainer.train_all_models(X_train, y_train)
# 评估模型
results = trainer.evaluate_models(X_test, y_test)
# 获取最佳模型
best_name, best_model = trainer.get_best_model(results)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression, LinearRegression
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.svm import SVC, SVR
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, mean_squared_error, classification_report
class ModelTrainer:
def __init__(self):
self.models = {}
self.trained_models = {}
def register_model(self, name, model, problem_type):
"""注册模型"""
self.models[name] = {
'model': model,
'problem_type': problem_type
}
print(f"注册模型:{name}({problem_type})")
def train_single_model(self, name, X_train, y_train):
"""训练单个模型"""
if name not in self.models:
raise ValueError(f"模型 {name} 未注册")
model_info = self.models[name]
model = model_info['model']
print(f"\n训练模型:{name}")
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
self.trained_models[name] = model
print(f"模型 {name} 训练完成")
return model
def train_all_models(self, X_train, y_train):
"""训练所有注册的模型"""
print("\n开始训练所有模型...")
for name in self.models.keys():
try:
self.train_single_model(name, X_train, y_train)
except Exception as e:
print(f"训练模型 {name} 时出错:{e}")
return self.trained_models
def evaluate_models(self, X_test, y_test):
"""评估所有训练好的模型"""
print("\n模型评估结果:")
print("-" * 50)
results = {}
for name, model in self.trained_models.items():
problem_type = self.models[name]['problem_type']
# 预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# 根据问题类型选择评估指标
if problem_type == 'classification':
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
results[name] = {'accuracy': accuracy}
print(f"{name}: 准确率 = {accuracy:.4f}")
# 详细报告
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
elif problem_type == 'regression':
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
rmse = np.sqrt(mse)
results[name] = {'mse': mse, 'rmse': rmse}
print(f"{name}: MSE = {mse:.4f}, RMSE = {rmse:.4f}")
print("-" * 50)
return results
def get_best_model(self, results, metric='accuracy'):
"""获取最佳模型"""
if not results:
return None
best_model_name = max(results.keys(), key=lambda x: results[x].get(metric, 0))
best_score = results[best_model_name][metric]
print(f"\n最佳模型:{best_model_name}({metric} = {best_score:.4f})")
return best_model_name, self.trained_models[best_model_name]
# 使用示例
trainer = ModelTrainer()
# 注册不同类型的模型
trainer.register_model('逻辑回归', LogisticRegression(random_state=42), 'classification')
trainer.register_model('随机森林', RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42), 'classification')
trainer.register_model('支持向量机', SVC(random_state=42), 'classification')
# 创建训练数据
X_train = splits['X_train']
y_train = splits['y_train']
X_test = splits['X_test']
y_test = splits['y_test']
# 训练所有模型
trained_models = trainer.train_all_models(X_train, y_train)
# 评估模型
results = trainer.evaluate_models(X_test, y_test)
# 获取最佳模型
best_name, best_model = trainer.get_best_model(results)
第五阶段:模型评估
评估指标选择
选择合适的评估指标就像选择合适的尺子,不同的指标适用于不同的场景。
常见评估指标
分类问题:
- 准确率(Accuracy):正确预测的比例
- 精确率(Precision):预测为正的样本中真正为正的比例
- 召回率(Recall):实际为正的样本中被正确预测为正的比例
- F1 分数:精确率和召回率的调和平均
回归问题:
- 均方误差(MSE):预测值与真实值差的平方的平均
- 均方根误差(RMSE):MSE 的平方根
- 平均绝对误差(MAE):预测值与真实值差的绝对值的平均
- R² 分数:模型解释的方差比例
模型评估示例
实例
# 模型评估示例
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import (
accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score,
confusion_matrix, roc_curve, auc
)
class ModelEvaluator:
def __init__(self):
self.evaluation_results = {}
def evaluate_classification(self, y_true, y_pred, y_prob=None, model_name="Model"):
"""评估分类模型"""
results = {}
# 基本指标
results['accuracy'] = accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
results['precision'] = precision_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')
results['recall'] = recall_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')
results['f1'] = f1_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')
print(f"\n{model_name} 分类评估结果:")
print(f"准确率:{results['accuracy']:.4f}")
print(f"精确率:{results['precision']:.4f}")
print(f"召回率:{results['recall']:.4f}")
print(f"F1 分数:{results['f1']:.4f}")
# 混淆矩阵
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
print(f"\n混淆矩阵:")
print(cm)
# ROC 曲线(如果有概率预测)
if y_prob is not None and len(np.unique(y_true)) == 2:
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_true, y_prob[:, 1])
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
results['roc_auc'] = roc_auc
# 绘制 ROC 曲线
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange', lw=2,
label=f'ROC 曲线 (AUC = {roc_auc:.2f})')
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=2, linestyle='--')
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('假正率')
plt.ylabel('真正率')
plt.title(f'{model_name} ROC 曲线')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
self.evaluation_results[model_name] = results
return results
def evaluate_regression(self, y_true, y_pred, model_name="Model"):
"""评估回归模型"""
results = {}
# 基本指标
mse = np.mean((y_true - y_pred) ** 2)
rmse = np.sqrt(mse)
mae = np.mean(np.abs(y_true - y_pred))
# R² 分数
ss_res = np.sum((y_true - y_pred) ** 2)
ss_tot = np.sum((y_true - np.mean(y_true)) ** 2)
r2 = 1 - (ss_res / ss_tot)
results['mse'] = mse
results['rmse'] = rmse
results['mae'] = mae
results['r2'] = r2
print(f"\n{model_name} 回归评估结果:")
print(f"均方误差 (MSE):{mse:.4f}")
print(f"均方根误差 (RMSE):{rmse:.4f}")
print(f"平均绝对误差 (MAE):{mae:.4f}")
print(f"R² 分数:{r2:.4f}")
# 绘制预测 vs 真实值
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.scatter(y_true, y_pred, alpha=0.6)
plt.plot([y_true.min(), y_true.max()], [y_true.min(), y_true.max()],
'r--', lw=2)
plt.xlabel('真实值')
plt.ylabel('预测值')
plt.title(f'{model_name} 预测 vs 真实值')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
self.evaluation_results[model_name] = results
return results
def compare_models(self):
"""比较所有评估过的模型"""
if not self.evaluation_results:
print("没有可比较的模型评估结果")
return
print("\n模型比较:")
print("-" * 50)
# 创建比较表格
comparison_data = []
for model_name, results in self.evaluation_results.items():
row = [model_name]
for metric, value in results.items():
row.append(f"{value:.4f}")
comparison_data.append(row)
# 打印表格
headers = ["模型名称"] + list(self.evaluation_results.values())[0].keys()
print("\t".join(headers))
for row in comparison_data:
print("\t".join(row))
# 使用示例
evaluator = ModelEvaluator()
# 评估分类模型
y_pred_class = best_model.predict(X_test)
y_prob_class = best_model.predict_proba(X_test)
evaluator.evaluate_classification(y_test, y_pred_class, y_prob_class, "最佳分类模型")
# 比较所有模型
evaluator.compare_models()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import (
accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score,
confusion_matrix, roc_curve, auc
)
class ModelEvaluator:
def __init__(self):
self.evaluation_results = {}
def evaluate_classification(self, y_true, y_pred, y_prob=None, model_name="Model"):
"""评估分类模型"""
results = {}
# 基本指标
results['accuracy'] = accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
results['precision'] = precision_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')
results['recall'] = recall_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')
results['f1'] = f1_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')
print(f"\n{model_name} 分类评估结果:")
print(f"准确率:{results['accuracy']:.4f}")
print(f"精确率:{results['precision']:.4f}")
print(f"召回率:{results['recall']:.4f}")
print(f"F1 分数:{results['f1']:.4f}")
# 混淆矩阵
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
print(f"\n混淆矩阵:")
print(cm)
# ROC 曲线(如果有概率预测)
if y_prob is not None and len(np.unique(y_true)) == 2:
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_true, y_prob[:, 1])
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
results['roc_auc'] = roc_auc
# 绘制 ROC 曲线
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange', lw=2,
label=f'ROC 曲线 (AUC = {roc_auc:.2f})')
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=2, linestyle='--')
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('假正率')
plt.ylabel('真正率')
plt.title(f'{model_name} ROC 曲线')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
self.evaluation_results[model_name] = results
return results
def evaluate_regression(self, y_true, y_pred, model_name="Model"):
"""评估回归模型"""
results = {}
# 基本指标
mse = np.mean((y_true - y_pred) ** 2)
rmse = np.sqrt(mse)
mae = np.mean(np.abs(y_true - y_pred))
# R² 分数
ss_res = np.sum((y_true - y_pred) ** 2)
ss_tot = np.sum((y_true - np.mean(y_true)) ** 2)
r2 = 1 - (ss_res / ss_tot)
results['mse'] = mse
results['rmse'] = rmse
results['mae'] = mae
results['r2'] = r2
print(f"\n{model_name} 回归评估结果:")
print(f"均方误差 (MSE):{mse:.4f}")
print(f"均方根误差 (RMSE):{rmse:.4f}")
print(f"平均绝对误差 (MAE):{mae:.4f}")
print(f"R² 分数:{r2:.4f}")
# 绘制预测 vs 真实值
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.scatter(y_true, y_pred, alpha=0.6)
plt.plot([y_true.min(), y_true.max()], [y_true.min(), y_true.max()],
'r--', lw=2)
plt.xlabel('真实值')
plt.ylabel('预测值')
plt.title(f'{model_name} 预测 vs 真实值')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
self.evaluation_results[model_name] = results
return results
def compare_models(self):
"""比较所有评估过的模型"""
if not self.evaluation_results:
print("没有可比较的模型评估结果")
return
print("\n模型比较:")
print("-" * 50)
# 创建比较表格
comparison_data = []
for model_name, results in self.evaluation_results.items():
row = [model_name]
for metric, value in results.items():
row.append(f"{value:.4f}")
comparison_data.append(row)
# 打印表格
headers = ["模型名称"] + list(self.evaluation_results.values())[0].keys()
print("\t".join(headers))
for row in comparison_data:
print("\t".join(row))
# 使用示例
evaluator = ModelEvaluator()
# 评估分类模型
y_pred_class = best_model.predict(X_test)
y_prob_class = best_model.predict_proba(X_test)
evaluator.evaluate_classification(y_test, y_pred_class, y_prob_class, "最佳分类模型")
# 比较所有模型
evaluator.compare_models()
第六阶段:模型部署
部署策略
模型部署是将模型投入实际使用的过程,就像将研发的产品推向市场一样。
部署方式
- 批量预测:定期处理大量数据
- 实时预测:在线服务,即时响应
- 嵌入式部署:将模型集成到现有系统
- 边缘部署:在设备端运行模型
模型部署示例
实例
# 模型部署示例
import pickle
import json
from datetime import datetime
class ModelDeployer:
def __init__(self):
self.deployed_models = {}
self.deployment_logs = []
def save_model(self, model, model_name, filepath=None):
"""保存模型"""
if filepath is None:
filepath = f"{model_name}.pkl"
with open(filepath, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(model, f)
print(f"模型 {model_name} 已保存到 {filepath}")
# 记录部署日志
log_entry = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'action': 'save_model',
'model_name': model_name,
'filepath': filepath
}
self.deployment_logs.append(log_entry)
return filepath
def load_model(self, model_name, filepath):
"""加载模型"""
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
model = pickle.load(f)
self.deployed_models[model_name] = model
print(f"模型 {model_name} 已从 {filepath} 加载")
# 记录部署日志
log_entry = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'action': 'load_model',
'model_name': model_name,
'filepath': filepath
}
self.deployment_logs.append(log_entry)
return model
def create_prediction_service(self, model_name, encoders=None, scaler=None):
"""创建预测服务"""
if model_name not in self.deployed_models:
raise ValueError(f"模型 {model_name} 未部署")
model = self.deployed_models[model_name]
def predict_service(input_data):
"""预测服务函数"""
try:
# 数据预处理
if encoders:
for col, encoder in encoders.items():
if col in input_data.columns:
input_data[col] = encoder.transform(input_data[col])
if scaler:
numeric_cols = input_data.select_dtypes(include=['number']).columns
input_data[numeric_cols] = scaler.transform(input_data[numeric_cols])
# 预测
prediction = model.predict(input_data)
# 如果是分类模型,也返回概率
if hasattr(model, 'predict_proba'):
probability = model.predict_proba(input_data)
return {
'prediction': prediction.tolist(),
'probability': probability.tolist(),
'status': 'success',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
else:
return {
'prediction': prediction.tolist(),
'status': 'success',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'error': str(e),
'status': 'error',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
# 记录服务创建日志
log_entry = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'action': 'create_service',
'model_name': model_name
}
self.deployment_logs.append(log_entry)
return predict_service
def monitor_model(self, model_name, input_data, true_labels=None):
"""监控模型性能"""
if model_name not in self.deployed_models:
raise ValueError(f"模型 {model_name} 未部署")
predict_service = self.create_prediction_service(model_name)
# 获取预测结果
result = predict_service(input_data)
# 监控信息
monitoring_info = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'model_name': model_name,
'input_shape': input_data.shape,
'prediction_count': len(result.get('prediction', [])),
'status': result.get('status', 'unknown')
}
# 如果有真实标签,计算性能指标
if true_labels is not None and 'prediction' in result:
predictions = result['prediction']
if len(predictions) == len(true_labels):
accuracy = accuracy_score(true_labels, predictions)
monitoring_info['accuracy'] = accuracy
print("模型监控信息:")
for key, value in monitoring_info.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
return monitoring_info
def get_deployment_logs(self):
"""获取部署日志"""
return self.deployment_logs
# 使用示例
deployer = ModelDeployer()
# 保存最佳模型
model_path = deployer.save_model(best_model, "best_classification_model")
# 加载模型
deployer.load_model("best_classification_model", model_path)
# 创建预测服务
prediction_service = deployer.create_prediction_service(
"best_classification_model", encoders, scaler
)
# 使用预测服务
test_input = X_test.head(5)
prediction_result = prediction_service(test_input)
print("\n预测结果:")
print(json.dumps(prediction_result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
# 监控模型
deployer.monitor_model("best_classification_model", test_input, y_test.head(5).values)
import pickle
import json
from datetime import datetime
class ModelDeployer:
def __init__(self):
self.deployed_models = {}
self.deployment_logs = []
def save_model(self, model, model_name, filepath=None):
"""保存模型"""
if filepath is None:
filepath = f"{model_name}.pkl"
with open(filepath, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(model, f)
print(f"模型 {model_name} 已保存到 {filepath}")
# 记录部署日志
log_entry = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'action': 'save_model',
'model_name': model_name,
'filepath': filepath
}
self.deployment_logs.append(log_entry)
return filepath
def load_model(self, model_name, filepath):
"""加载模型"""
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
model = pickle.load(f)
self.deployed_models[model_name] = model
print(f"模型 {model_name} 已从 {filepath} 加载")
# 记录部署日志
log_entry = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'action': 'load_model',
'model_name': model_name,
'filepath': filepath
}
self.deployment_logs.append(log_entry)
return model
def create_prediction_service(self, model_name, encoders=None, scaler=None):
"""创建预测服务"""
if model_name not in self.deployed_models:
raise ValueError(f"模型 {model_name} 未部署")
model = self.deployed_models[model_name]
def predict_service(input_data):
"""预测服务函数"""
try:
# 数据预处理
if encoders:
for col, encoder in encoders.items():
if col in input_data.columns:
input_data[col] = encoder.transform(input_data[col])
if scaler:
numeric_cols = input_data.select_dtypes(include=['number']).columns
input_data[numeric_cols] = scaler.transform(input_data[numeric_cols])
# 预测
prediction = model.predict(input_data)
# 如果是分类模型,也返回概率
if hasattr(model, 'predict_proba'):
probability = model.predict_proba(input_data)
return {
'prediction': prediction.tolist(),
'probability': probability.tolist(),
'status': 'success',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
else:
return {
'prediction': prediction.tolist(),
'status': 'success',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'error': str(e),
'status': 'error',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
# 记录服务创建日志
log_entry = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'action': 'create_service',
'model_name': model_name
}
self.deployment_logs.append(log_entry)
return predict_service
def monitor_model(self, model_name, input_data, true_labels=None):
"""监控模型性能"""
if model_name not in self.deployed_models:
raise ValueError(f"模型 {model_name} 未部署")
predict_service = self.create_prediction_service(model_name)
# 获取预测结果
result = predict_service(input_data)
# 监控信息
monitoring_info = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'model_name': model_name,
'input_shape': input_data.shape,
'prediction_count': len(result.get('prediction', [])),
'status': result.get('status', 'unknown')
}
# 如果有真实标签,计算性能指标
if true_labels is not None and 'prediction' in result:
predictions = result['prediction']
if len(predictions) == len(true_labels):
accuracy = accuracy_score(true_labels, predictions)
monitoring_info['accuracy'] = accuracy
print("模型监控信息:")
for key, value in monitoring_info.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
return monitoring_info
def get_deployment_logs(self):
"""获取部署日志"""
return self.deployment_logs
# 使用示例
deployer = ModelDeployer()
# 保存最佳模型
model_path = deployer.save_model(best_model, "best_classification_model")
# 加载模型
deployer.load_model("best_classification_model", model_path)
# 创建预测服务
prediction_service = deployer.create_prediction_service(
"best_classification_model", encoders, scaler
)
# 使用预测服务
test_input = X_test.head(5)
prediction_result = prediction_service(test_input)
print("\n预测结果:")
print(json.dumps(prediction_result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
# 监控模型
deployer.monitor_model("best_classification_model", test_input, y_test.head(5).values)
完整流程示例
实例
# 完整的机器学习流程示例
class MLProjectPipeline:
def __init__(self):
self.data_collector = DataCollector()
self.data_preparer = None
self.model_trainer = ModelTrainer()
self.model_evaluator = ModelEvaluator()
self.model_deployer = ModelDeployer()
def run_complete_pipeline(self, target_column):
"""运行完整的机器学习流水线"""
print("=" * 60)
print("机器学习项目完整流程")
print("=" * 60)
# 1. 数据收集
print("\n第1步:数据收集")
print("-" * 30)
user_data = self.data_collector.collect_user_data(1000)
behavior_data = self.data_collector.collect_behavior_data(5000)
# 合并数据(简化示例)
merged_data = pd.merge(user_data, behavior_data, on='user_id', how='inner')
# 创建目标变量(示例:是否购买)
merged_data['purchased'] = (merged_data['behavior_type'] == '购买').astype(int)
# 2. 数据准备
print("\n第2步:数据准备")
print("-" * 30)
# 选择特征列
feature_columns = ['age', 'gender', 'city', 'duration']
if all(col in merged_data.columns for col in feature_columns):
data_for_ml = merged_data[feature_columns + ['purchased']].copy()
# 处理类别变量
data_for_ml['gender'] = data_for_ml['gender'].map({'男': 0, '女': 1})
data_for_ml['city'] = data_for_ml['city'].map({'北京': 0, '上海': 1, '广州': 2})
# 数据准备
self.data_preparer = DataPreparer(data_for_ml)
splits, encoders, scaler = self.data_preparer.prepare_pipeline('purchased')
# 3. 模型训练
print("\n第3步:模型训练")
print("-" * 30)
# 注册模型
self.model_trainer.register_model(
'逻辑回归', LogisticRegression(random_state=42), 'classification'
)
self.model_trainer.register_model(
'随机森林', RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42), 'classification'
)
# 训练模型
trained_models = self.model_trainer.train_all_models(
splits['X_train'], splits['y_train']
)
# 4. 模型评估
print("\n第4步:模型评估")
print("-" * 30)
results = self.model_trainer.evaluate_models(
splits['X_test'], splits['y_test']
)
best_name, best_model = self.model_trainer.get_best_model(results)
# 5. 模型部署
print("\n第5步:模型部署")
print("-" * 30)
# 保存模型
model_path = self.model_deployer.save_model(best_model, "production_model")
# 创建预测服务
prediction_service = self.model_deployer.create_prediction_service(
"production_model"
)
# 测试预测服务
test_input = splits['X_test'].head(3)
prediction_result = prediction_service(test_input)
print("\n预测服务测试结果:")
print(json.dumps(prediction_result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("机器学习项目流程完成!")
print("=" * 60)
return {
'data': data_for_ml,
'splits': splits,
'best_model': best_model,
'best_model_name': best_name,
'evaluation_results': results,
'prediction_service': prediction_service
}
else:
print("数据列不完整,无法继续流程")
return None
# 运行完整流程
pipeline = MLProjectPipeline()
project_results = pipeline.run_complete_pipeline('purchased')
class MLProjectPipeline:
def __init__(self):
self.data_collector = DataCollector()
self.data_preparer = None
self.model_trainer = ModelTrainer()
self.model_evaluator = ModelEvaluator()
self.model_deployer = ModelDeployer()
def run_complete_pipeline(self, target_column):
"""运行完整的机器学习流水线"""
print("=" * 60)
print("机器学习项目完整流程")
print("=" * 60)
# 1. 数据收集
print("\n第1步:数据收集")
print("-" * 30)
user_data = self.data_collector.collect_user_data(1000)
behavior_data = self.data_collector.collect_behavior_data(5000)
# 合并数据(简化示例)
merged_data = pd.merge(user_data, behavior_data, on='user_id', how='inner')
# 创建目标变量(示例:是否购买)
merged_data['purchased'] = (merged_data['behavior_type'] == '购买').astype(int)
# 2. 数据准备
print("\n第2步:数据准备")
print("-" * 30)
# 选择特征列
feature_columns = ['age', 'gender', 'city', 'duration']
if all(col in merged_data.columns for col in feature_columns):
data_for_ml = merged_data[feature_columns + ['purchased']].copy()
# 处理类别变量
data_for_ml['gender'] = data_for_ml['gender'].map({'男': 0, '女': 1})
data_for_ml['city'] = data_for_ml['city'].map({'北京': 0, '上海': 1, '广州': 2})
# 数据准备
self.data_preparer = DataPreparer(data_for_ml)
splits, encoders, scaler = self.data_preparer.prepare_pipeline('purchased')
# 3. 模型训练
print("\n第3步:模型训练")
print("-" * 30)
# 注册模型
self.model_trainer.register_model(
'逻辑回归', LogisticRegression(random_state=42), 'classification'
)
self.model_trainer.register_model(
'随机森林', RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42), 'classification'
)
# 训练模型
trained_models = self.model_trainer.train_all_models(
splits['X_train'], splits['y_train']
)
# 4. 模型评估
print("\n第4步:模型评估")
print("-" * 30)
results = self.model_trainer.evaluate_models(
splits['X_test'], splits['y_test']
)
best_name, best_model = self.model_trainer.get_best_model(results)
# 5. 模型部署
print("\n第5步:模型部署")
print("-" * 30)
# 保存模型
model_path = self.model_deployer.save_model(best_model, "production_model")
# 创建预测服务
prediction_service = self.model_deployer.create_prediction_service(
"production_model"
)
# 测试预测服务
test_input = splits['X_test'].head(3)
prediction_result = prediction_service(test_input)
print("\n预测服务测试结果:")
print(json.dumps(prediction_result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("机器学习项目流程完成!")
print("=" * 60)
return {
'data': data_for_ml,
'splits': splits,
'best_model': best_model,
'best_model_name': best_name,
'evaluation_results': results,
'prediction_service': prediction_service
}
else:
print("数据列不完整,无法继续流程")
return None
# 运行完整流程
pipeline = MLProjectPipeline()
project_results = pipeline.run_complete_pipeline('purchased')

点我分享笔记