机器学习应用
机器学习应用可以分为几个主要领域,每个领域都有其独特的应用场景和挑战:
- 计算机视觉:让机器"看懂"世界
- 自然语言处理:让机器"理解"人类语言
- 推荐系统:个性化推荐内容
- 预测分析:预测未来趋势和结果
- 异常检测:发现不寻常的模式
为什么这些应用需要机器学习?
想象一下,如果用传统编程方法来解决这些问题:
- 人脸识别:需要编写无数规则来描述人脸的各种变化(角度、光线、表情等)
- 语言翻译:需要为每种语言组合编写庞大的词典和语法规则
- 推荐系统:需要人工分析每个用户的喜好和每件商品的特征
机器学习让计算机能够从大量数据中自动学习这些复杂模式,大大简化了问题解决的过程。
计算机视觉应用
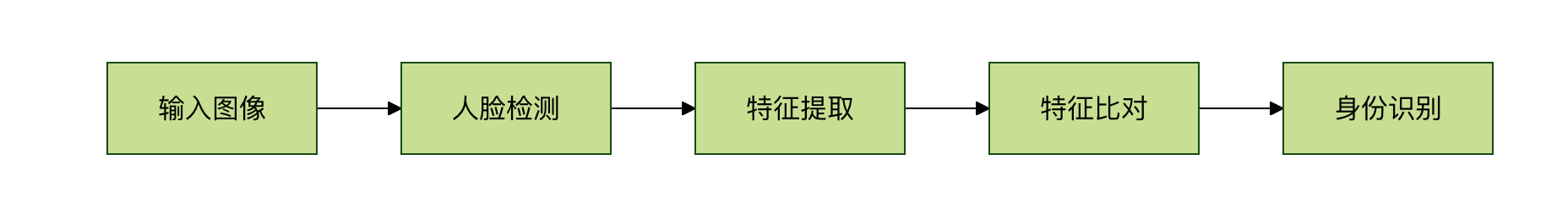
人脸识别
应用场景:手机解锁、门禁系统、身份验证
工作原理:
- 检测图像中的人脸位置
- 提取人脸特征(眼睛间距、鼻子形状等)
- 与数据库中的人脸特征比对
自动驾驶
应用场景:特斯拉 Autopilot、百度 Apollo、谷歌 Waymo
核心任务:
- 物体检测:识别车辆、行人、交通标志
- 车道检测:确定车道边界
- 路径规划:决定行驶路线
实例
# 自动驾驶中的物体检测示例(概念代码)
import cv2
import numpy as np
def detect_objects(image):
"""
检测图像中的物体(车辆、行人、交通标志等)
"""
# 1. 预处理图像
processed_image = preprocess_image(image)
# 2. 使用训练好的深度学习模型检测物体
# 这里使用预训练的 YOLO 模型作为示例
boxes, classes, scores = yolo_model.detect(processed_image)
# 3. 过滤低置信度的检测结果
valid_detections = filter_detections(boxes, classes, scores)
# 4. 在图像上绘制检测结果
result_image = draw_detections(image, valid_detections)
return result_image, valid_detections
# 实际应用中,这只是整个自动驾驶系统的一个组件
# 还需要结合传感器融合、路径规划等多个模块
import cv2
import numpy as np
def detect_objects(image):
"""
检测图像中的物体(车辆、行人、交通标志等)
"""
# 1. 预处理图像
processed_image = preprocess_image(image)
# 2. 使用训练好的深度学习模型检测物体
# 这里使用预训练的 YOLO 模型作为示例
boxes, classes, scores = yolo_model.detect(processed_image)
# 3. 过滤低置信度的检测结果
valid_detections = filter_detections(boxes, classes, scores)
# 4. 在图像上绘制检测结果
result_image = draw_detections(image, valid_detections)
return result_image, valid_detections
# 实际应用中,这只是整个自动驾驶系统的一个组件
# 还需要结合传感器融合、路径规划等多个模块
医疗影像诊断
应用场景:X光片分析、CT扫描、病理切片分析
优势:
- 比人类医生更少疲劳
- 能发现人眼难以察觉的细微变化
- 可以快速处理大量影像
自然语言处理应用
智能助手
应用场景:Siri、小爱同学、天猫精灵
核心功能:
- 语音识别:将语音转换为文字
- 意图理解:理解用户想要什么
- 对话管理:维持连贯的对话
实例
# 智能助手的工作流程(简化示例)
import speech_recognition as sr
from textblob import TextBlob
class SmartAssistant:
def __init__(self):
self.recognizer = sr.Recognizer()
def listen_and_respond(self):
"""监听用户语音并回应"""
with sr.Microphone() as source:
print("正在聆听...")
audio = self.recognizer.listen(source)
try:
# 1. 语音识别
text = self.recognizer.recognize_google(audio, language='zh-CN')
print(f"用户说:{text}")
# 2. 意图理解
intent = self.understand_intent(text)
# 3. 生成回应
response = self.generate_response(intent, text)
print(f"助手回应:{response}")
return response
except sr.UnknownValueError:
return "抱歉,我没有听清楚,请再说一次"
def understand_intent(self, text):
"""理解用户意图"""
# 简化的意图识别
if "天气" in text:
return "weather"
elif "时间" in text:
return "time"
elif "笑话" in text:
return "joke"
else:
return "unknown"
def generate_response(self, intent, text):
"""根据意图生成回应"""
if intent == "weather":
return "今天晴天,温度25度"
elif intent == "time":
from datetime import datetime
return f"现在时间是{datetime.now().strftime('%H:%M')}"
elif intent == "joke":
return "为什么程序员喜欢黑夜?因为没有 bug!"
else:
return "抱歉,我还在学习中,无法理解这个问题"
# 使用示例
assistant = SmartAssistant()
# assistant.listen_and_respond() # 实际运行时取消注释
import speech_recognition as sr
from textblob import TextBlob
class SmartAssistant:
def __init__(self):
self.recognizer = sr.Recognizer()
def listen_and_respond(self):
"""监听用户语音并回应"""
with sr.Microphone() as source:
print("正在聆听...")
audio = self.recognizer.listen(source)
try:
# 1. 语音识别
text = self.recognizer.recognize_google(audio, language='zh-CN')
print(f"用户说:{text}")
# 2. 意图理解
intent = self.understand_intent(text)
# 3. 生成回应
response = self.generate_response(intent, text)
print(f"助手回应:{response}")
return response
except sr.UnknownValueError:
return "抱歉,我没有听清楚,请再说一次"
def understand_intent(self, text):
"""理解用户意图"""
# 简化的意图识别
if "天气" in text:
return "weather"
elif "时间" in text:
return "time"
elif "笑话" in text:
return "joke"
else:
return "unknown"
def generate_response(self, intent, text):
"""根据意图生成回应"""
if intent == "weather":
return "今天晴天,温度25度"
elif intent == "time":
from datetime import datetime
return f"现在时间是{datetime.now().strftime('%H:%M')}"
elif intent == "joke":
return "为什么程序员喜欢黑夜?因为没有 bug!"
else:
return "抱歉,我还在学习中,无法理解这个问题"
# 使用示例
assistant = SmartAssistant()
# assistant.listen_and_respond() # 实际运行时取消注释
机器翻译
应用场景:谷歌翻译、百度翻译、有道翻译
工作原理:
- 将源语言文本编码为数字表示
- 通过神经网络学习语言间的映射关系
- 解码为目标语言文本
情感分析
应用场景:产品评论分析、社交媒体监控、客户反馈处理
实例
# 情感分析示例
from textblob import TextBlob
import jieba
def analyze_sentiment_chinese(text):
"""
中文情感分析示例
"""
# 使用 jieba 分词
words = jieba.cut(text)
word_list = " ".join(words)
# 这里简化处理,实际应用中需要专门的中文情感分析模型
# 可以使用 SnowNLP、BERT-Chinese 等库
# 模拟情感分析结果
positive_words = ["好", "棒", "喜欢", "满意", "推荐"]
negative_words = ["差", "坏", "讨厌", "失望", "不推荐"]
pos_count = sum(1 for word in positive_words if word in text)
neg_count = sum(1 for word in negative_words if word in text)
if pos_count > neg_count:
return "正面情感"
elif neg_count > pos_count:
return "负面情感"
else:
return "中性情感"
# 测试示例
reviews = [
"这个产品真的很棒,我非常喜欢!",
"质量太差了,完全不值得购买。",
"还可以,没什么特别的。"
]
for review in reviews:
sentiment = analyze_sentiment_chinese(review)
print(f"评论:{review}")
print(f"情感:{sentiment}")
print("---")
from textblob import TextBlob
import jieba
def analyze_sentiment_chinese(text):
"""
中文情感分析示例
"""
# 使用 jieba 分词
words = jieba.cut(text)
word_list = " ".join(words)
# 这里简化处理,实际应用中需要专门的中文情感分析模型
# 可以使用 SnowNLP、BERT-Chinese 等库
# 模拟情感分析结果
positive_words = ["好", "棒", "喜欢", "满意", "推荐"]
negative_words = ["差", "坏", "讨厌", "失望", "不推荐"]
pos_count = sum(1 for word in positive_words if word in text)
neg_count = sum(1 for word in negative_words if word in text)
if pos_count > neg_count:
return "正面情感"
elif neg_count > pos_count:
return "负面情感"
else:
return "中性情感"
# 测试示例
reviews = [
"这个产品真的很棒,我非常喜欢!",
"质量太差了,完全不值得购买。",
"还可以,没什么特别的。"
]
for review in reviews:
sentiment = analyze_sentiment_chinese(review)
print(f"评论:{review}")
print(f"情感:{sentiment}")
print("---")
推荐系统应用
电商推荐
应用场景:淘宝商品推荐、亚马逊推荐
推荐策略:
- 协同过滤:基于用户行为相似性推荐
- 内容推荐:基于商品特征相似性推荐
- 混合推荐:结合多种策略
实例
# 简单的协同过滤推荐示例
import numpy as np
# 用户-商品评分矩阵(行是用户,列是商品)
ratings = np.array([
[5, 3, 0, 1], # 用户1对商品1、2、4的评分
[4, 0, 0, 1], # 用户2对商品1、4的评分
[1, 1, 0, 5], # 用户3对商品1、2、4的评分
[1, 0, 0, 4], # 用户4对商品1、4的评分
[0, 1, 5, 4], # 用户5对商品2、3、4的评分
])
def user_similarity(user1, user2):
"""计算两个用户的相似度(余弦相似度)"""
# 找到两个用户都评分的商品
common_items = np.where((user1 > 0) & (user2 > 0))[0]
if len(common_items) == 0:
return 0
# 计算余弦相似度
user1_ratings = user1[common_items]
user2_ratings = user2[common_items]
dot_product = np.dot(user1_ratings, user2_ratings)
norm1 = np.linalg.norm(user1_ratings)
norm2 = np.linalg.norm(user2_ratings)
if norm1 == 0 or norm2 == 0:
return 0
return dot_product / (norm1 * norm2)
def recommend_items(user_id, ratings_matrix, k=2):
"""为指定用户推荐商品"""
user_ratings = ratings_matrix[user_id]
# 计算该用户与其他用户的相似度
similarities = []
for i, other_user in enumerate(ratings_matrix):
if i != user_id:
sim = user_similarity(user_ratings, other_user)
similarities.append((i, sim))
# 按相似度排序
similarities.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
# 找到用户未评分的商品
unrated_items = np.where(user_ratings == 0)[0]
# 预测用户对未评分商品的评分
predictions = []
for item_id in unrated_items:
weighted_sum = 0
similarity_sum = 0
for similar_user_id, similarity in similarities[:k]:
if similarity > 0 and ratings_matrix[similar_user_id][item_id] > 0:
weighted_sum += similarity * ratings_matrix[similar_user_id][item_id]
similarity_sum += similarity
if similarity_sum > 0:
predicted_rating = weighted_sum / similarity_sum
predictions.append((item_id, predicted_rating))
# 按预测评分排序
predictions.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return predictions[:3] # 返回前3个推荐
# 为用户0推荐商品
user_id = 0
recommendations = recommend_items(user_id, ratings)
print(f"为用户{user_id}推荐的商品:")
for item_id, predicted_rating in recommendations:
print(f"商品{item_id + 1},预测评分:{predicted_rating:.2f}")
import numpy as np
# 用户-商品评分矩阵(行是用户,列是商品)
ratings = np.array([
[5, 3, 0, 1], # 用户1对商品1、2、4的评分
[4, 0, 0, 1], # 用户2对商品1、4的评分
[1, 1, 0, 5], # 用户3对商品1、2、4的评分
[1, 0, 0, 4], # 用户4对商品1、4的评分
[0, 1, 5, 4], # 用户5对商品2、3、4的评分
])
def user_similarity(user1, user2):
"""计算两个用户的相似度(余弦相似度)"""
# 找到两个用户都评分的商品
common_items = np.where((user1 > 0) & (user2 > 0))[0]
if len(common_items) == 0:
return 0
# 计算余弦相似度
user1_ratings = user1[common_items]
user2_ratings = user2[common_items]
dot_product = np.dot(user1_ratings, user2_ratings)
norm1 = np.linalg.norm(user1_ratings)
norm2 = np.linalg.norm(user2_ratings)
if norm1 == 0 or norm2 == 0:
return 0
return dot_product / (norm1 * norm2)
def recommend_items(user_id, ratings_matrix, k=2):
"""为指定用户推荐商品"""
user_ratings = ratings_matrix[user_id]
# 计算该用户与其他用户的相似度
similarities = []
for i, other_user in enumerate(ratings_matrix):
if i != user_id:
sim = user_similarity(user_ratings, other_user)
similarities.append((i, sim))
# 按相似度排序
similarities.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
# 找到用户未评分的商品
unrated_items = np.where(user_ratings == 0)[0]
# 预测用户对未评分商品的评分
predictions = []
for item_id in unrated_items:
weighted_sum = 0
similarity_sum = 0
for similar_user_id, similarity in similarities[:k]:
if similarity > 0 and ratings_matrix[similar_user_id][item_id] > 0:
weighted_sum += similarity * ratings_matrix[similar_user_id][item_id]
similarity_sum += similarity
if similarity_sum > 0:
predicted_rating = weighted_sum / similarity_sum
predictions.append((item_id, predicted_rating))
# 按预测评分排序
predictions.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return predictions[:3] # 返回前3个推荐
# 为用户0推荐商品
user_id = 0
recommendations = recommend_items(user_id, ratings)
print(f"为用户{user_id}推荐的商品:")
for item_id, predicted_rating in recommendations:
print(f"商品{item_id + 1},预测评分:{predicted_rating:.2f}")
视频推荐
应用场景:抖音、YouTube、Netflix
特点:
- 实时推荐(根据用户当前行为调整)
- 多模态数据(视频内容、用户行为、时间等)
- 冷启动问题处理
预测分析应用
金融风控
应用场景:信用卡欺诈检测、贷款审批
实例
# 简单的欺诈检测示例
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 模拟交易数据
# 特征:交易金额、交易时间、商户类型、地点等
# 标签:0=正常,1=欺诈
np.random.seed(42)
# 生成模拟数据
n_samples = 1000
n_features = 4
# 正常交易
normal_transactions = np.random.normal(loc=[100, 14, 2, 3], scale=[50, 4, 1, 1],
size=(int(n_samples * 0.95), n_features))
# 欺诈交易(通常金额异常、时间异常等)
fraud_transactions = np.random.normal(loc=[500, 3, 4, 1], scale=[200, 2, 1, 0.5],
size=(int(n_samples * 0.05), n_features))
# 合并数据并添加标签
X = np.vstack([normal_transactions, fraud_transactions])
y = np.hstack([np.zeros(len(normal_transactions)), np.ones(len(fraud_transactions))])
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 训练随机森林模型
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 评估模型
accuracy = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print(f"模型准确率:{accuracy:.2f}")
# 预测新交易
new_transaction = np.array([[450, 2, 4, 1]]) # 异常交易
fraud_probability = model.predict_proba(new_transaction)[0][1]
print(f"新交易是欺诈的概率:{fraud_probability:.2f}")
if fraud_probability > 0.5:
print("警告:检测到可疑交易!")
else:
print("交易正常。")
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 模拟交易数据
# 特征:交易金额、交易时间、商户类型、地点等
# 标签:0=正常,1=欺诈
np.random.seed(42)
# 生成模拟数据
n_samples = 1000
n_features = 4
# 正常交易
normal_transactions = np.random.normal(loc=[100, 14, 2, 3], scale=[50, 4, 1, 1],
size=(int(n_samples * 0.95), n_features))
# 欺诈交易(通常金额异常、时间异常等)
fraud_transactions = np.random.normal(loc=[500, 3, 4, 1], scale=[200, 2, 1, 0.5],
size=(int(n_samples * 0.05), n_features))
# 合并数据并添加标签
X = np.vstack([normal_transactions, fraud_transactions])
y = np.hstack([np.zeros(len(normal_transactions)), np.ones(len(fraud_transactions))])
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 训练随机森林模型
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 评估模型
accuracy = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print(f"模型准确率:{accuracy:.2f}")
# 预测新交易
new_transaction = np.array([[450, 2, 4, 1]]) # 异常交易
fraud_probability = model.predict_proba(new_transaction)[0][1]
print(f"新交易是欺诈的概率:{fraud_probability:.2f}")
if fraud_probability > 0.5:
print("警告:检测到可疑交易!")
else:
print("交易正常。")
股价预测
应用场景:量化交易、投资决策
挑战:
- 市场噪声大
- 非平稳时间序列
- 受多种因素影响
异常检测应用
网络安全
应用场景:入侵检测、恶意软件识别
工作原理:
- 学习正常网络流量模式
- 检测偏离正常模式的行为
- 触发警报或阻断
工业质检
应用场景:产品缺陷检测、设备故障预测
实例
# 简单的异常检测示例
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 模拟传感器数据(正常数据 + 少量异常)
np.random.seed(42)
# 正常数据:设备正常运行时的传感器读数
normal_data = np.random.normal(loc=10, scale=1, size=(200, 2))
# 异常数据:设备故障时的传感器读数
anomaly_data = np.random.normal(loc=[15, 5], scale=[1, 1], size=(10, 2))
# 合并数据
all_data = np.vstack([normal_data, anomaly_data])
# 使用孤立森林进行异常检测
model = IsolationForest(contamination=0.05, random_state=42)
predictions = model.fit_predict(all_data)
# 可视化结果
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
normal_points = all_data[predictions == 1]
anomaly_points = all_data[predictions == -1]
plt.scatter(normal_points[:, 0], normal_points[:, 1],
c='blue', label='正常数据')
plt.scatter(anomaly_points[:, 0], anomaly_points[:, 1],
c='red', label='异常数据')
plt.xlabel('传感器1读数')
plt.ylabel('传感器2读数')
plt.title('设备运行状态异常检测')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
print(f"检测到 {len(anomaly_points)} 个异常点")
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 模拟传感器数据(正常数据 + 少量异常)
np.random.seed(42)
# 正常数据:设备正常运行时的传感器读数
normal_data = np.random.normal(loc=10, scale=1, size=(200, 2))
# 异常数据:设备故障时的传感器读数
anomaly_data = np.random.normal(loc=[15, 5], scale=[1, 1], size=(10, 2))
# 合并数据
all_data = np.vstack([normal_data, anomaly_data])
# 使用孤立森林进行异常检测
model = IsolationForest(contamination=0.05, random_state=42)
predictions = model.fit_predict(all_data)
# 可视化结果
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
normal_points = all_data[predictions == 1]
anomaly_points = all_data[predictions == -1]
plt.scatter(normal_points[:, 0], normal_points[:, 1],
c='blue', label='正常数据')
plt.scatter(anomaly_points[:, 0], anomaly_points[:, 1],
c='red', label='异常数据')
plt.xlabel('传感器1读数')
plt.ylabel('传感器2读数')
plt.title('设备运行状态异常检测')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
print(f"检测到 {len(anomaly_points)} 个异常点")

点我分享笔记