Vue3 Pinia 入门教程
在 Vue3 中,状态管理是一个绕不开的话题。
Pinia 是 Vue.js 的轻量级状态管理库,它让你能够在组件之间共享和管理状态,我们可以把 Pinia 想象成一个全局的数据仓库,所有组件都可以从这里获取数据或者更新数据。
本章节我们要介绍的是 Vue3 官方推荐的状态管理库 —— Pinia,相比 Vuex,Pinia 提供了更简洁、更符合 Vue3 组合式 API 思维的状态管理方案。
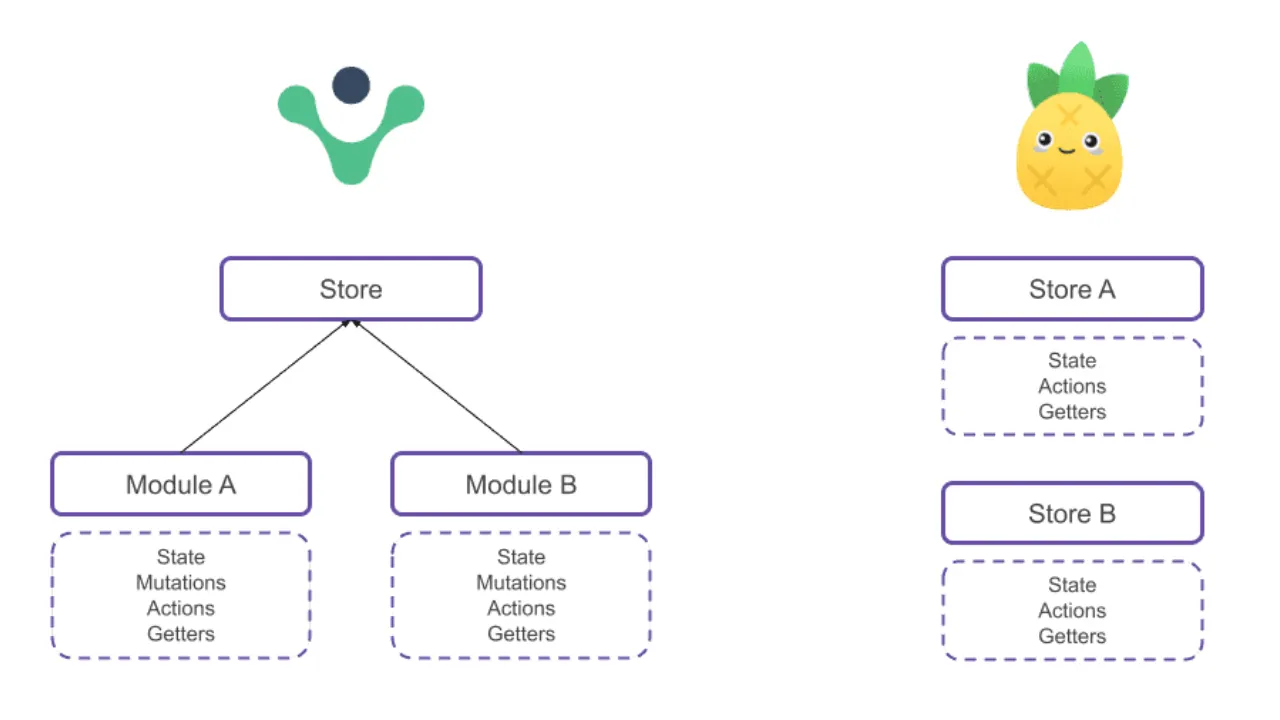
下图对比了两者的结构差异:
- Vuex 采用单仓库加多级模块的树状结构,层级固定,依赖 mutations,整体更重。
- Pinia 则由多个独立 store 组成,扁平、轻量、不分模块,无命名空间负担。
Pinia 核心特点:
- 支持 Vue2 和 Vue3
- 极简的 API 设计
- 完整的 TypeScript 支持
- 支持组合式 API
- 模块化设计,无需嵌套模块
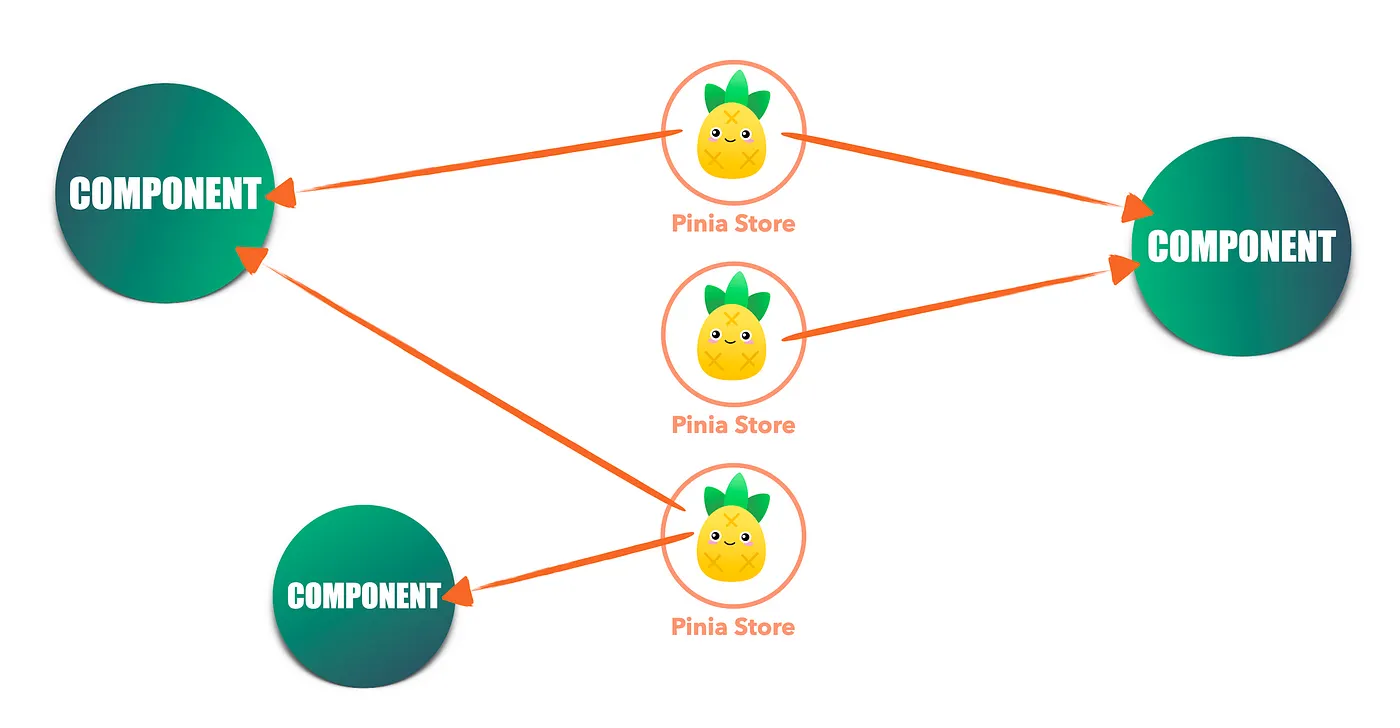
Pinia 的扁平结构让组件可以直接连到任意 store,各取所需,不经过树状模块,也不走命名空间路径,状态流动简单直接,耦合度低。
安装与配置
用 Vite 创建项目:
npm create vite@latest vue-pinia-demo --template vue cd vue-pinia-demo npm install
安装 Pinia
首先,在你的 Vue3 项目中安装 Pinia:
npm install pinia # 或者 yarn add pinia
Pinia 有三部分:
- state:存数据
- getters:算派生数据
- actions:执行逻辑、修改 state
配置 Pinia
在 src/main.js 或 src/main.ts 中配置 Pinia:
实例
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
// 创建 Pinia 实例
const pinia = createPinia()
// 创建 Vue 应用
const app = createApp(App)
// 使用 Pinia
app.use(pinia)
app.mount('#app')
创建第一个 Store
Store 就是 Pinia 中的数据仓库,我们来创建一个简单的计数器 Store。
定义 Store
新建 src/stores/useCounter.js:
实例
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
// 使用 defineStore 定义 store
// 第一个参数是 store 的唯一 ID
// 第二个参数是 store 的配置选项
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
// state: 定义 store 的状态数据
state: () => ({
count: 0,
name: '我的计数器'
}),
// getters: 定义基于 state 的计算属性
getters: {
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
// 使用 this 访问其他 getter
doubleCountPlusOne() {
return this.doubleCount + 1
}
},
// actions: 定义修改 state 的方法
actions: {
increment() {
this.count++
},
decrement() {
this.count--
},
// 可以接收参数
incrementBy(amount) {
this.count += amount
},
// 异步 action
async incrementAsync() {
// 模拟异步操作
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000))
this.count++
}
}
})
Store 的结构说明
让我们通过一个表格来理解 Store 的各个部分:
| 部分 | 作用 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| state | 定义存储的数据 | count: 0 |
| getters | 基于 state 的计算属性 | doubleCount: state => state.count * 2 |
| actions | 修改 state 的方法 | increment() { this.count++ } |
在组件中使用 Store
基本使用
src/components/CounterComponent.vue 组件代码如下:
实例
<template>
<div class="counter">
<h3>{{ store.name }}</h3>
<p>当前计数: {{ store.count }}</p>
<p>双倍计数: {{ store.doubleCount }}</p>
<p>双倍加一: {{ store.doubleCountPlusOne }}</p>
<button @click="store.increment()">+1</button>
<button @click="store.decrement()">-1</button>
<button @click="store.incrementBy(5)">+5</button>
<button @click="store.incrementAsync()">异步 +1</button>
<button @click="reset">重置</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useCounterStore } from '@/stores/counter'
// 在 setup 中使用 store
const store = useCounterStore()
// 重置状态的方法
function reset() {
store.$reset() // $reset 方法可以重置 state 到初始值
}
</script>
修改 src/App.vue 代码如下:
实例
import CounterComponent from './components/CounterComponent.vue'
</script>
<template>
<CounterComponent />
</template>
整个项目结构:

执行 npm run dev 命令,在浏览器访问 http://localhost:5173/,查看效果:

响应式解构
如果你想在模板中直接使用 state 的属性,可以使用 storeToRefs:
实例
<div>
<p>计数: {{ count }}</p>
<p>名称: {{ name }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
import { useCounterStore } from '@/stores/counter'
const store = useCounterStore()
// 使用 storeToRefs 保持响应式
const { count, name } = storeToRefs(store)
// 注意:直接解构会失去响应式!
// 错误写法:const { count, name } = store
</script>
组合式 API 风格的 Store
Pinia 也支持使用组合式 API 的风格来定义 Store:
实例
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', () => {
// state
const user = ref(null)
const isLoggedIn = ref(false)
// getters
const userName = computed(() => user.value?.name || '游客')
const userAge = computed(() => user.value?.age || 0)
// actions
function login(userData) {
user.value = userData
isLoggedIn.value = true
}
function logout() {
user.value = null
isLoggedIn.value = false
}
return {
user,
isLoggedIn,
userName,
userAge,
login,
logout
}
})
Store 之间的交互
多个 Store 之间可以相互调用:
实例
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useCartStore = defineStore('cart', {
state: () => ({
items: []
}),
actions: {
addItem(product) {
this.items.push(product)
// 调用其他 store 的 action
const userStore = useUserStore()
if (userStore.isLoggedIn) {
// 同步到用户购物车
this.syncToUserCart()
}
}
}
})
实际应用示例:购物车
让我们创建一个完整的购物车示例:
实例
export const useProductStore = defineStore('products', {
state: () => ({
products: [
{ id: 1, name: '笔记本电脑', price: 5999, stock: 10 },
{ id: 2, name: '智能手机', price: 3999, stock: 20 },
{ id: 3, name: '无线耳机', price: 299, stock: 50 }
]
}),
getters: {
// 根据 ID 获取商品
getProductById: (state) => (id) => {
return state.products.find(product => product.id === id)
},
// 获取有库存的商品
availableProducts: (state) => {
return state.products.filter(product => product.stock > 0)
}
}
})
实例
export const useCartStore = defineStore('cart', {
state: () => ({
items: [], // { productId, quantity }
discount: 0
}),
getters: {
// 购物车商品总数
totalItems: (state) => {
return state.items.reduce((total, item) => total + item.quantity, 0)
},
// 购物车总金额
totalPrice: (state) => {
const productStore = useProductStore()
return state.items.reduce((total, item) => {
const product = productStore.getProductById(item.productId)
return total + (product?.price || 0) * item.quantity
}, 0)
},
// 折后总价
finalPrice: (state) => {
return state.totalPrice * (1 - state.discount / 100)
}
},
actions: {
// 添加商品到购物车
addToCart(productId, quantity = 1) {
const existingItem = this.items.find(item => item.productId === productId)
if (existingItem) {
existingItem.quantity += quantity
} else {
this.items.push({ productId, quantity })
}
},
// 从购物车移除商品
removeFromCart(productId) {
this.items = this.items.filter(item => item.productId !== productId)
},
// 清空购物车
clearCart() {
this.items = []
this.discount = 0
},
// 设置折扣
setDiscount(percent) {
this.discount = Math.max(0, Math.min(100, percent))
}
}
})
在组件中使用购物车
实例
<template>
<div class="shopping-cart">
<h3>购物车 ({{ cart.totalItems }} 件商品)</h3>
<div v-if="cart.items.length === 0">
<p>购物车为空</p>
</div>
<div v-else>
<div v-for="item in cartItems" :key="item.product.id" class="cart-item">
<span>{{ item.product.name }}</span>
<span>¥{{ item.product.price }}</span>
<span>数量: {{ item.quantity }}</span>
<span>小计: ¥{{ item.product.price * item.quantity }}</span>
<button @click="cart.removeFromCart(item.product.id)">删除</button>
</div>
<div class="cart-summary">
<p>总价: ¥{{ cart.totalPrice }}</p>
<p v-if="cart.discount > 0">折扣: {{ cart.discount }}%</p>
<p>实付: ¥{{ cart.finalPrice }}</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { computed } from 'vue'
import { useCartStore } from '@/stores/cart'
import { useProductStore } from '@/stores/products'
const cart = useCartStore()
const products = useProductStore()
// 计算购物车商品详情
const cartItems = computed(() => {
return cart.items.map(item => ({
product: products.getProductById(item.productId),
quantity: item.quantity
})).filter(item => item.product) // 过滤掉不存在的商品
})
</script>
最佳实践和注意事项
1. Store 命名规范
实例
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', { /* ... */ })
export const useProductStore = defineStore('products', { /* ... */ })
// 避免的命名
export const userStore = defineStore('user', { /* ... */ }) // 缺少 use 前缀
2. 状态初始化
实例
state: () => ({
items: [],
loading: false,
error: null
})
// 不推荐:直接使用对象
state: {
items: [] // 这会导致所有实例共享同一个数组!
}
3. 异步操作处理
实例
async fetchUserData(userId) {
this.loading = true
this.error = null
try {
const response = await api.getUser(userId)
this.user = response.data
} catch (error) {
this.error = error.message
} finally {
this.loading = false
}
}
}
4. 数据持久化
对于需要持久化的数据,可以使用插件:
npm install pinia-plugin-persistedstate
实例
import piniaPluginPersistedstate from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'
const pinia = createPinia()
pinia.use(piniaPluginPersistedstate)
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {
state: () => ({
token: '',
userInfo: {}
}),
// 启用持久化
persist: true
})
Pinia API
| 分类 | API | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 创建 | defineStore |
定义一个独立的 store,包含 state / getters / actions |
| 实例化 | createPinia |
创建 Pinia 根实例,用于 app.use() |
| 组件使用 | useStore()(用户自定义,如 useUserStore) |
调用某个 store,返回响应式 state、getter、action |
| 状态 | state |
返回一个对象函数,用于定义可变全局状态 |
| 状态操作 | store.$state |
直接读写整个 state(对象级) |
| 状态操作 | store.$patch() |
批量修改 state,支持对象和函数两种模式 |
| 状态替换 | store.$reset() |
重置为初始 state,仅在 setup 方式定义时可用 |
| 状态订阅 | store.$subscribe() |
监听 state 变化,适合本地持久化 |
| Action 调用 | store.$onAction() |
监听 action 调用前后,可做日志、埋点 |
| Getter | getters |
派生数据,基于 state 自动缓存 |
| 插件 | pinia.use() |
注册插件,扩展 store 能力 |
| 定义方式 | defineStore(id, options) |
Options API 写法 |
| 定义方式 | defineStore(id, () => {...}) |
Setup 写法,返回 state / getter / action |
| Store 属性 | store.$id |
当前 store 的唯一标识 |
| Store 属性 | store.$ready(部分版本) |
Store 初始化完成后的状态标记 |
| 持久化(插件) | persist |
启用存储插件(如 localStorage) |
| 工具函数 | storeToRefs() |
将 state / getter 转为 refs,保留响应式 |
更多内容参考 Pinia 官网:https://pinia.vuejs.org/

点我分享笔记