Node.js Promise
Promise 是 Node.js 中处理异步操作的核心概念之一。
Promise 提供了一种更优雅的方式来管理异步代码,避免了传统的回调地狱(Callback Hell)问题。
本文将详细介绍 Promise 的概念、用法和常见模式。
什么是 Promise?
Promise 是一个表示异步操作最终完成或失败的对象。它有三种状态:
- Pending(等待中):初始状态,既不是成功,也不是失败
- Fulfilled(已成功):操作成功完成
- Rejected(已失败):操作失败
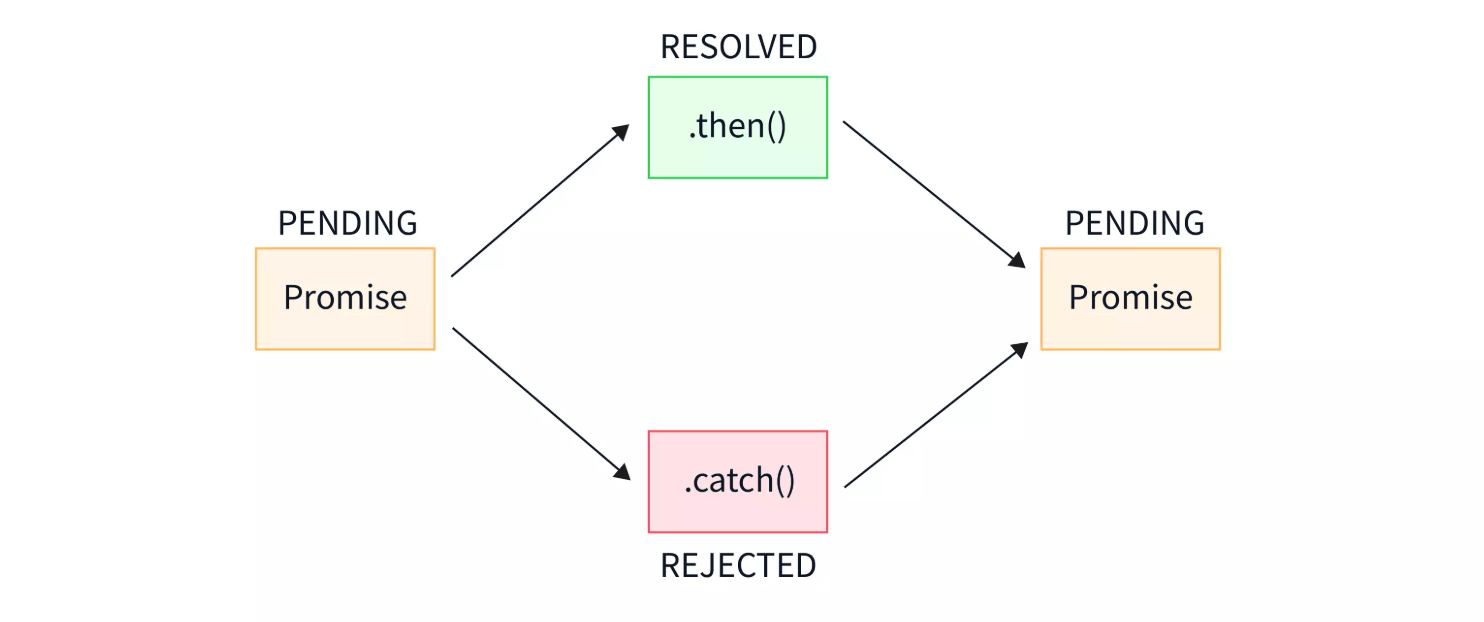
Promise 的状态一旦改变(从 pending 变为 fulfilled 或 rejected),就不会再改变。
创建 Promise
在 Node.js 中,可以使用 Promise 构造函数创建新的 Promise 对象:
实例
const myPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 异步操作
const success = true; // 假设这是异步操作的结果
if (success) {
resolve('操作成功!'); // 状态变为 fulfilled
} else {
reject('操作失败!'); // 状态变为 rejected
}
});
// 异步操作
const success = true; // 假设这是异步操作的结果
if (success) {
resolve('操作成功!'); // 状态变为 fulfilled
} else {
reject('操作失败!'); // 状态变为 rejected
}
});
使用 Promise
Promise 提供了 .then() 和 .catch() 方法来处理成功和失败的情况:
实例
myPromise
.then((result) => {
console.log(result); // 输出:"操作成功!"
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error); // 输出:"操作失败!"
});
.then((result) => {
console.log(result); // 输出:"操作成功!"
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error); // 输出:"操作失败!"
});
Promise 链式调用
Promise 的强大之处在于可以链式调用多个异步操作:
实例
function asyncOperation1() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve('第一步完成'), 1000);
});
}
function asyncOperation2(data) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(`${data}, 第二步完成`), 1000);
});
}
asyncOperation1()
.then((result) => asyncOperation2(result))
.then((finalResult) => {
console.log(finalResult); // 输出:"第一步完成, 第二步完成"
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('链式中出错:', error);
});
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve('第一步完成'), 1000);
});
}
function asyncOperation2(data) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(`${data}, 第二步完成`), 1000);
});
}
asyncOperation1()
.then((result) => asyncOperation2(result))
.then((finalResult) => {
console.log(finalResult); // 输出:"第一步完成, 第二步完成"
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('链式中出错:', error);
});
Promise 的静态方法
Promise 提供了一些有用的静态方法:
Promise.all()
等待所有 Promise 完成,或任意一个 Promise 失败:
实例
const promise1 = Promise.resolve('第一个');
const promise2 = Promise.resolve('第二个');
Promise.all([promise1, promise2])
.then((results) => {
console.log(results); // 输出:['第一个', '第二个']
});
const promise2 = Promise.resolve('第二个');
Promise.all([promise1, promise2])
.then((results) => {
console.log(results); // 输出:['第一个', '第二个']
});
Promise.race()
返回最先完成或失败的 Promise:
实例
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 500, '第一个'));
const promise2 = new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 100, '第二个'));
Promise.race([promise1, promise2])
.then((result) => {
console.log(result); // 输出:"第二个"
});
const promise2 = new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 100, '第二个'));
Promise.race([promise1, promise2])
.then((result) => {
console.log(result); // 输出:"第二个"
});
错误处理
Promise 的错误处理可以通过 .catch() 或 .then() 的第二个参数实现:
实例
someAsyncFunction()
.then(
(result) => { /* 处理成功 */ },
(error) => { /* 处理失败 */ }
);
// 或者
someAsyncFunction()
.then((result) => { /* 处理成功 */ })
.catch((error) => { /* 处理所有错误 */ });
.then(
(result) => { /* 处理成功 */ },
(error) => { /* 处理失败 */ }
);
// 或者
someAsyncFunction()
.then((result) => { /* 处理成功 */ })
.catch((error) => { /* 处理所有错误 */ });
async/await 语法
ES2017 引入了 async/await 语法,让 Promise 的使用更加直观:
实例
async function runOperations() {
try {
const result1 = await asyncOperation1();
const result2 = await asyncOperation2(result1);
console.log(result2);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
runOperations();
try {
const result1 = await asyncOperation1();
const result2 = await asyncOperation2(result1);
console.log(result2);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
runOperations();
最佳实践
- 总是处理错误:不要忽略
.catch()或 try-catch - 避免嵌套:使用链式调用或 async/await 保持代码扁平
- 命名 Promise:给 Promise 变量起有意义的名称
- 返回 Promise:在函数中返回 Promise 以便链式调用

点我分享笔记